As the world faces challenges related to food security, environmental sustainability, and animal welfare, lab-grown meat is emerging as a promising solution. This innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and consume meat, offering numerous benefits for both people and the planet. Here are 13 fascinating facts about lab-grown meat and why it could be the answer to our prayers.
1. Lab-Grown Meat Is Real Meat
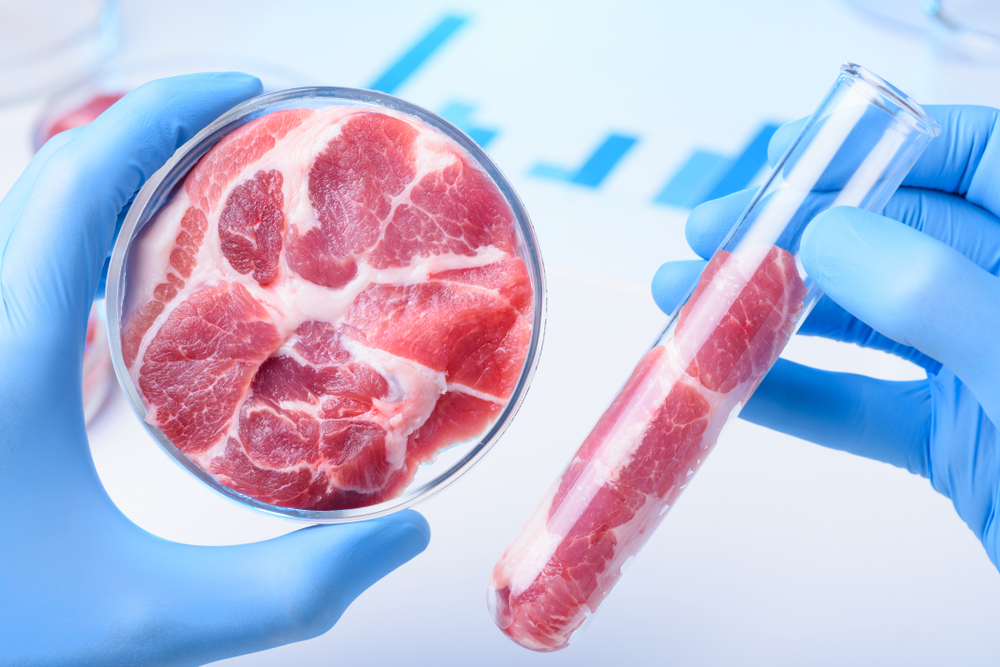
Despite being produced in a lab, lab-grown meat is, in fact, real meat. It is made by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, replicating the natural growth process that occurs inside an animal. This means that lab-grown meat contains the same proteins, fats, and nutrients as conventionally raised meat, making it a viable alternative without compromising on taste or nutrition. According to Vision of Humanity, lab-grown meat is considered real meat due to its cellular composition.
What’s fascinating is that lab-grown meat can be created from a variety of animal cells, including beef, chicken, and pork. This makes it possible to produce meat without the need for traditional farming, reducing the need for raising and slaughtering animals. Lab-grown meat offers a solution that could satisfy meat lovers without the ethical concerns of animal husbandry.
2. It’s Environmentally Friendly

One of the most compelling reasons for supporting lab-grown meat is its potential environmental impact. Traditional meat production is resource-intensive, requiring vast amounts of water, land, and energy. In contrast, lab-grown meat uses fewer resources in some aspects, such as water consumption. However, recent studies suggest that current production methods might not always be environmentally superior. According to Nature, lab-grown meat could reduce environmental impacts like methane emissions from cows, but it also depends on the energy sources and materials used in production.
Additionally, lab-grown meat produces fewer greenhouse gases in some scenarios, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. By eliminating the need for large-scale livestock farming, we can reduce deforestation and the depletion of natural habitats. This sustainable method of meat production could be a crucial part of the global effort to combat environmental degradation
3. It’s Healthier Than Conventional Meat

Lab-grown meat offers the possibility of a healthier alternative to conventional meat. Since it is produced in a controlled environment, it can be engineered to have fewer harmful substances, such as excess fat or hormones, commonly found in traditionally farmed meat. Scientists can also manipulate the composition of the meat to increase its nutritional value, such as adding healthy omega-3 fatty acids or reducing saturated fats.
According to Frontiers in Nutrition, lab-grown meat can offer nutritional advantages over conventional meat by controlling its composition. Moreover, lab-grown meat is free from antibiotics and other chemicals often used in factory farming to prevent disease in livestock. This means that consumers could enjoy meat without the risks associated with the use of these substances in traditional meat production, making lab-grown meat a cleaner and healthier option.
4. It’s Ethical

Lab-grown meat addresses significant ethical concerns related to animal welfare. Traditional meat production involves the raising, breeding, and slaughtering of animals, often under harsh conditions. Lab-grown meat, on the other hand, does not require animals to be raised or killed. Instead, it uses animal cells to grow the meat, making it a cruelty-free alternative.
This ethical advantage could be a game-changer for people who have chosen plant-based diets due to concerns about animal cruelty but miss the taste and texture of meat. Lab-grown meat offers a solution that satisfies meat cravings while aligning with a more humane approach to food production. According to Northeastern University, lab-grown meat avoids some of the ethical pitfalls of traditional meat production by using animal cells instead of slaughtering animals.
5. It Reduces the Risk of Zoonotic Diseases

Zoonotic diseases, which can be transmitted from animals to humans, have been a significant concern for public health, with outbreaks like bird flu and swine flu threatening global populations. Since lab-grown meat is produced in a sterile environment, there is less risk of contamination from diseases that typically spread through livestock. This makes lab-grown meat a safer option for consumption compared to conventionally farmed meat.
By reducing the need for live animals in meat production, lab-grown meat also reduces the risk of diseases like E. coli, Salmonella, and mad cow disease, which have been linked to animal farming. This could play a key role in improving food safety and protecting public health worldwide.
6. It Could Solve Global Food Security Issues

Lab-grown meat could play a crucial role in addressing the growing challenge of global food security. With the world’s population expected to reach 9 billion by 2050, the demand for food—particularly protein—will rise dramatically. Lab-grown meat can be produced at a scale that meets this demand, offering a more efficient and scalable solution to feed the world.
Furthermore, lab-grown meat can be produced in areas where traditional farming is difficult or unsustainable. This means that even regions facing droughts, land degradation, or limited access to arable land could still produce meat, contributing to more equitable access to protein around the world.
7. It’s More Efficient Than Traditional Meat Production
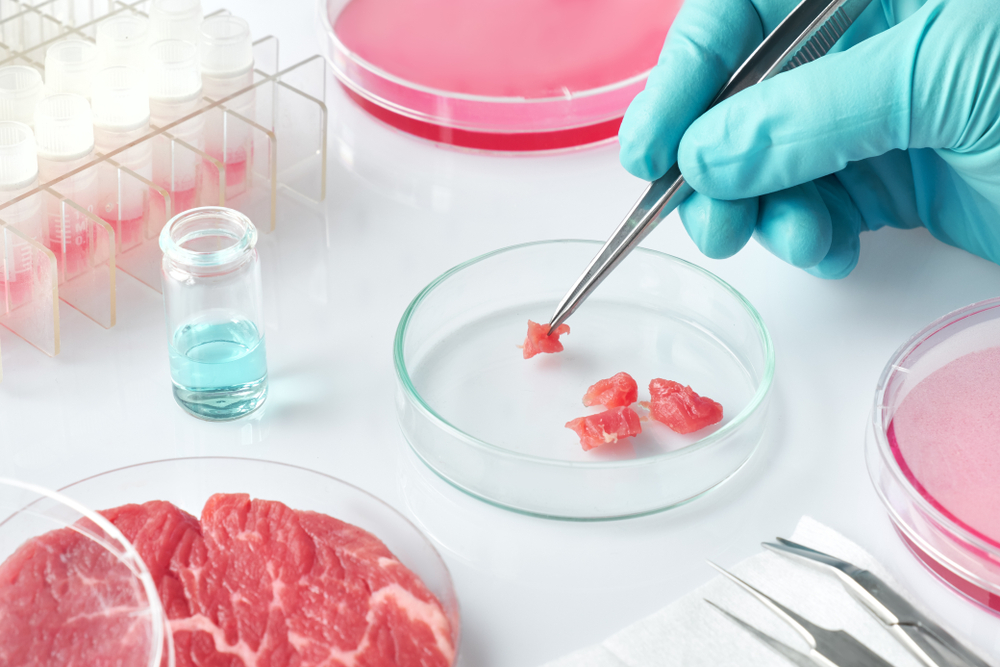

Producing lab-grown meat is far more efficient than traditional livestock farming. It requires fewer resources, such as water, land, and feed, to produce the same amount of meat. It’s estimated that lab-grown meat could reduce land use by up to 99% compared to traditional beef farming.
This efficiency not only helps save natural resources but also makes the process of meat production more sustainable. As the world continues to face increasing demands for food and resources, lab-grown meat provides a way to meet these needs with minimal environmental impact, making it a far more sustainable option for the future.
8. It’s Likely to Be More Affordable in the Future

While lab-grown meat is currently expensive to produce, technological advancements and increased demand are expected to drive costs down. As production methods improve and economies of scale come into play, lab-grown meat could become much more affordable in the coming years. The price of lab-grown meat has already dropped significantly since its first successful production in 2013.
In the future, lab-grown meat could be as affordable as conventionally produced meat, making it accessible to a wider population. As costs continue to decrease, lab-grown meat could become a mainstream product that is both affordable and sustainable for consumers worldwide.
9. It Has the Potential to End Factory Farming

One of the most significant benefits of lab-grown meat is its potential to end factory farming. Factory farms are notorious for their unethical practices, including overcrowding, poor living conditions, and environmental degradation. Lab-grown meat could eliminate the need for factory farming by providing a way to produce meat without the need for raising animals in confined spaces.
By transitioning to lab-grown meat, we could reduce the negative impact of factory farming on both animals and the environment. This shift could lead to a more ethical, sustainable, and humane food system that aligns with the growing demand for cruelty-free products.
10. It Can Be Tailored to Consumer Preferences
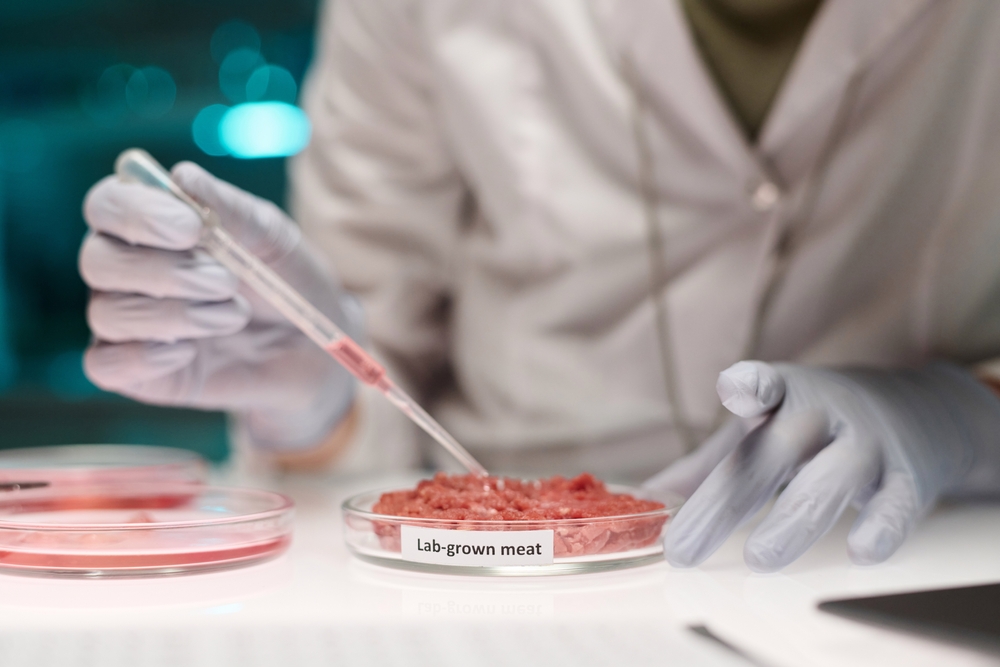
Lab-grown meat offers the unique advantage of being customizable to suit consumer preferences. Scientists can manipulate the production process to create meat that matches specific textures, flavors, and fat content. This means that lab-grown meat can be designed to replicate the taste and texture of traditional meat to perfection, catering to a wide variety of tastes.
Additionally, lab-grown meat can be engineered to meet the dietary needs of different populations. For example, it could be produced with higher levels of certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids or vitamins, to address specific health concerns. This level of customization is something that conventional meat production cannot offer, making lab-grown meat a versatile and adaptable option for consumers.
11. It Reduces Waste and Byproducts
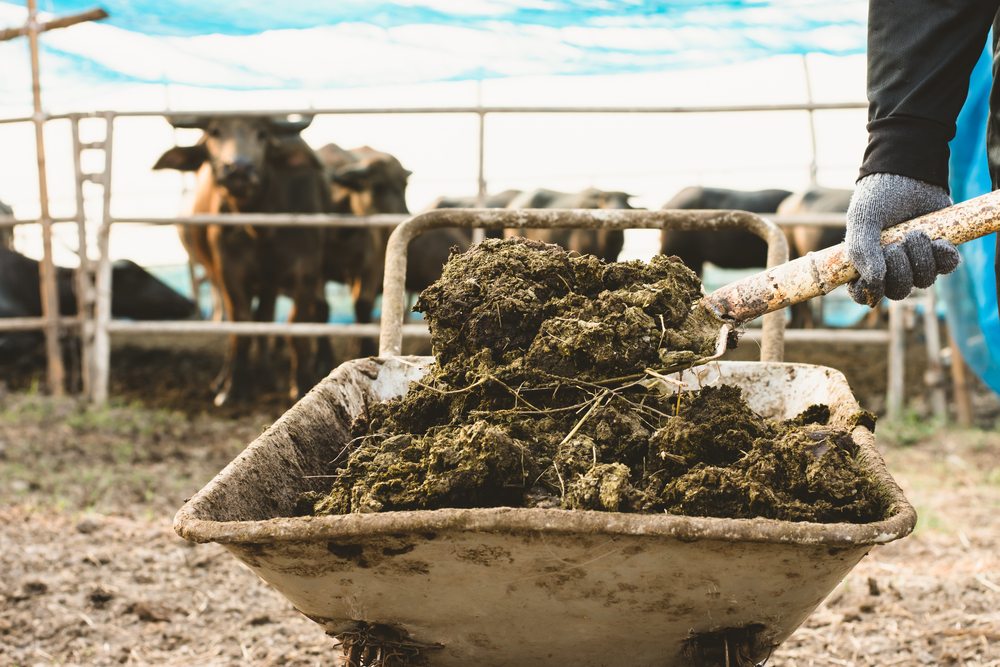

Traditional meat production generates significant waste and byproducts, including manure, slaughterhouse waste, and unused animal parts. In contrast, lab-grown meat is produced in a controlled environment with minimal waste. Since only the necessary animal cells are used, there is far less waste generated, and byproducts like bones and offal are not produced.
This waste reduction is not only environmentally beneficial but also makes the meat production process more efficient. By eliminating the need for animal slaughter and reducing waste, lab-grown meat could help create a cleaner, more sustainable food system.
12. It’s Already Being Tested in Restaurants

Lab-grown meat is no longer just a concept—it’s already being tested in restaurants around the world. In 2020, lab-grown chicken was served to customers in Singapore, making it the first country to approve the sale of cultured meat. Other restaurants in countries like the United States and Europe have also started experimenting with lab-grown meat, providing consumers with a chance to taste the future of food.
As lab-grown meat becomes more widely accepted, it could be available in supermarkets and restaurants globally. Shortly, you might find lab-grown burgers or steaks on your menu, offering a sustainable, ethical, and delicious alternative to traditional meat products.
13. It Could Be the Key to Solving Global Hunger
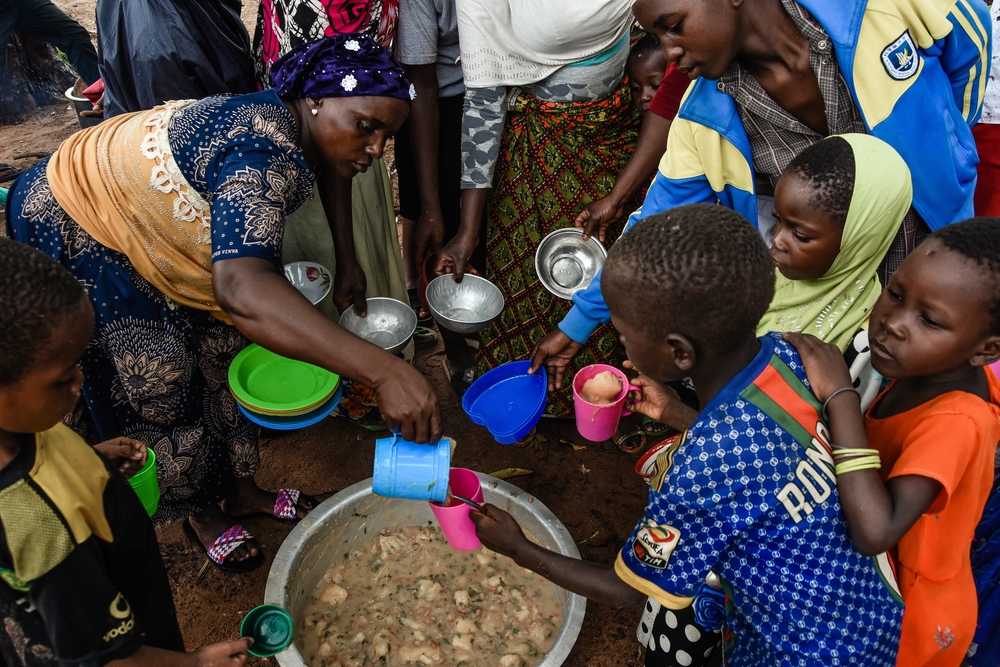

Lab-grown meat has the potential to address one of the world’s most pressing issues: global hunger. With its ability to be produced efficiently and at scale, lab-grown meat can provide an abundant source of protein to regions with limited access to traditional meat production. This could play a significant role in feeding millions of people in developing countries, where food insecurity is a constant challenge.
Moreover, lab-grown meat can be produced in a way that is not dependent on climate or geography, making it an ideal solution for areas where agricultural production is limited. By ensuring that everyone has access to a reliable and sustainable source of protein, lab-grown meat could help alleviate hunger and promote global food security.
Abisola is a communication specialist with a background in language studies and project management. She believes in the power of words to effectively connect with her audience and address their needs. With her strong foundation in both language and project management, she crafts messages that are not only clear and engaging but also aligned with strategic goals. Whether through content creation, storytelling, or communication planning, Abisola uses her expertise to ensure that her messages resonate and deliver lasting value to her audience.


