Across the globe, there are communities where people seem to defy the typical aging process, living well into their 100s with energy, vitality, and a strong sense of community. These long-lived populations have earned the title of “Blue Zones”—regions where the rate of centenarians is much higher than the global average. What’s their secret? While genetics play a role, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and mindset are crucial. Here’s a look at 15 cultures that live a ridiculously long time—and what they do differently to achieve longevity.
1. Sardinia, Italy
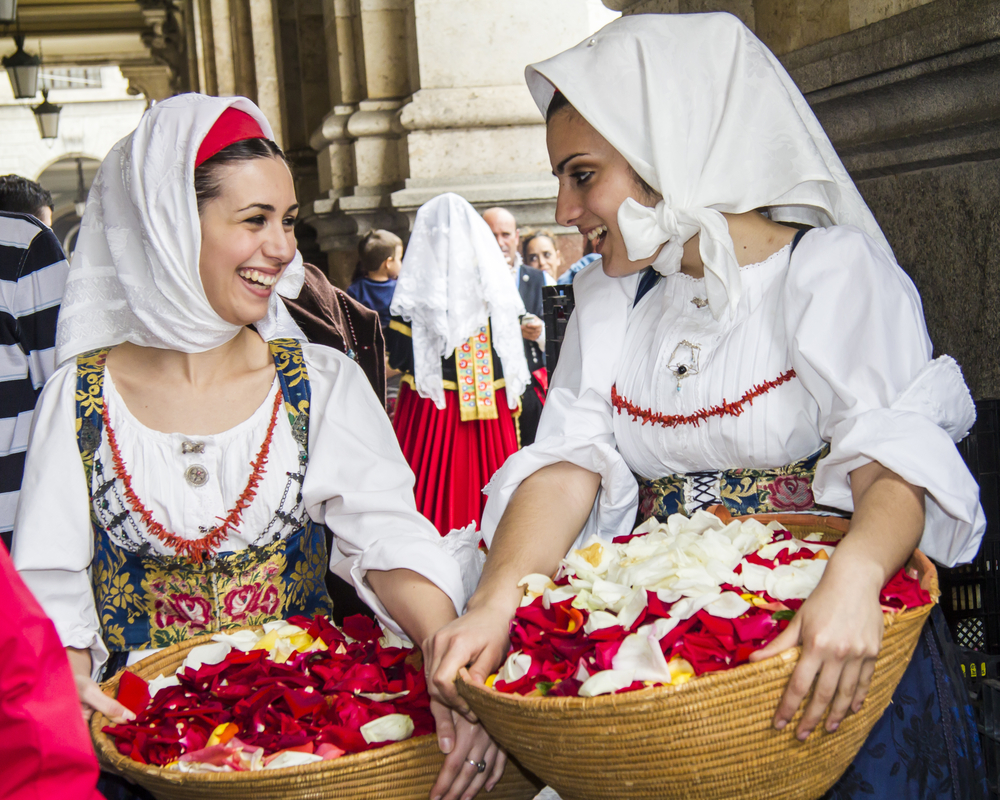

Sardinia, particularly the mountainous region of Nuoro, boasts a high number of male centenarians. One of the key factors in their longevity is a diet that emphasizes whole grains, vegetables, and moderate wine consumption, often paired with sheep’s milk cheese. Sardinians also lead physically active lives, working in the fields and walking frequently, which keeps them fit even into their older years.
Strong family ties and a sense of community are also essential to Sardinian culture. The elderly are respected and integrated into family life, which provides emotional support and a sense of purpose that contributes to their longevity. According to Medical Xpress, shorter stature among Sardinian men has been linked to increased longevity, supporting previous studies that found height to be a factor in lifespan.
2. Okinawa, Japan
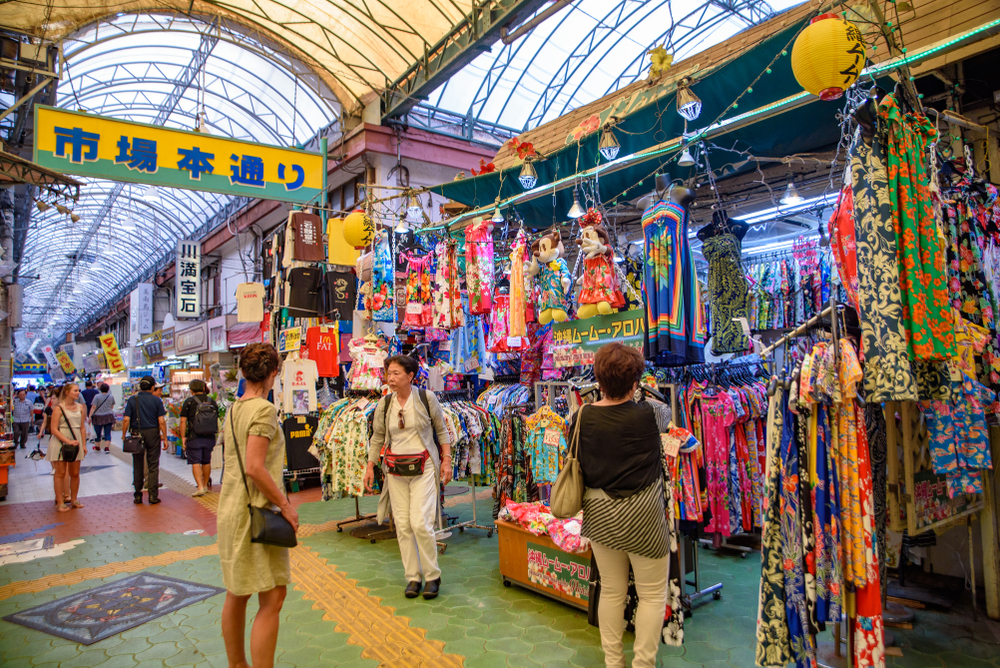

Okinawa is home to one of the world’s highest concentrations of centenarians. People in Okinawa have a strong sense of purpose, a practice known as “ikigai,” which is thought to keep them mentally sharp and emotionally fulfilled. Their diet is rich in vegetables, tofu, and sweet potatoes, while their portion sizes are smaller, following the principle of “hara hachi bu,” or eating until you’re 80% full. They also prioritize close social bonds, engaging in daily activities with friends and family.
The combination of a plant-based diet, mindful eating habits, and social connection plays a key role in their long lifespans. Staying active both physically and mentally is also part of their daily routine, contributing to their overall health and longevity. According to the Okinawa Research Center for Longevity Science, the Okinawa Centenarian Study has been investigating the health of the aging population since 1975, highlighting the importance of lifestyle factors in longevity.
3. Ikaria, Greece
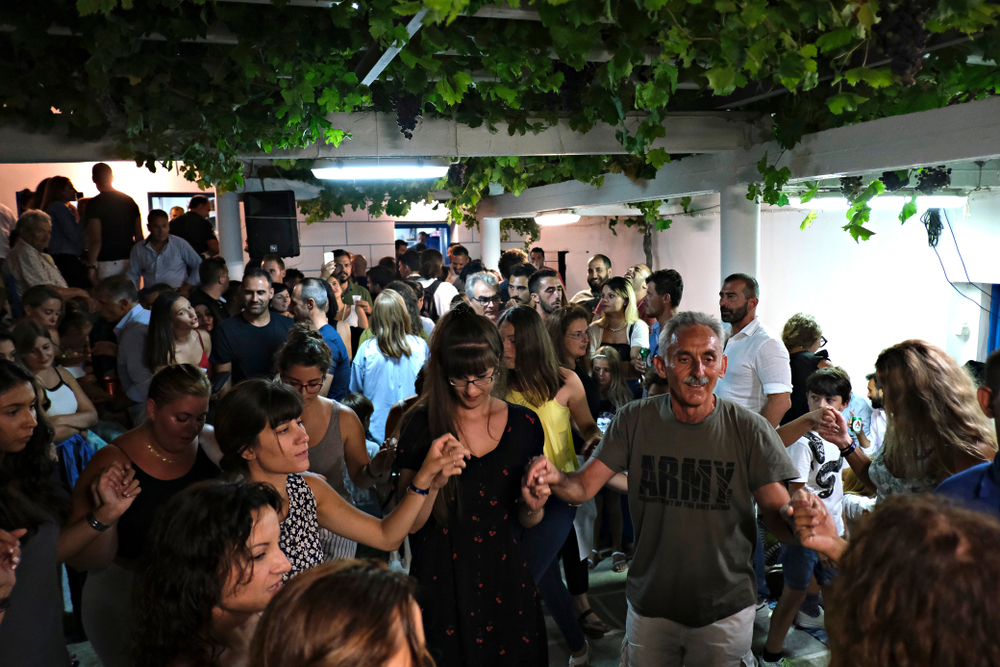

Ikaria, a Greek island in the Aegean Sea, has one of the highest rates of people living into their 90s and beyond. The Ikarian diet is rich in vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, with olive oil as a primary fat source. Their Mediterranean diet, low in processed foods, contributes to heart health and longevity. In addition to their diet, Ikarian people maintain a relaxed pace of life and regularly take naps, reducing stress and promoting better health.
The sense of community and a slower, more intentional lifestyle is key to their longevity. The islanders also stay socially active, engaging in communal events and maintaining a close-knit network of family and friends, which helps keep their mental health strong. According to Dr. Rachel Dew, Ikarians’ lifestyle, including regular napping and a Mediterranean diet, contributes significantly to their longevity.
4. Nicoya Peninsula, Costa Rica
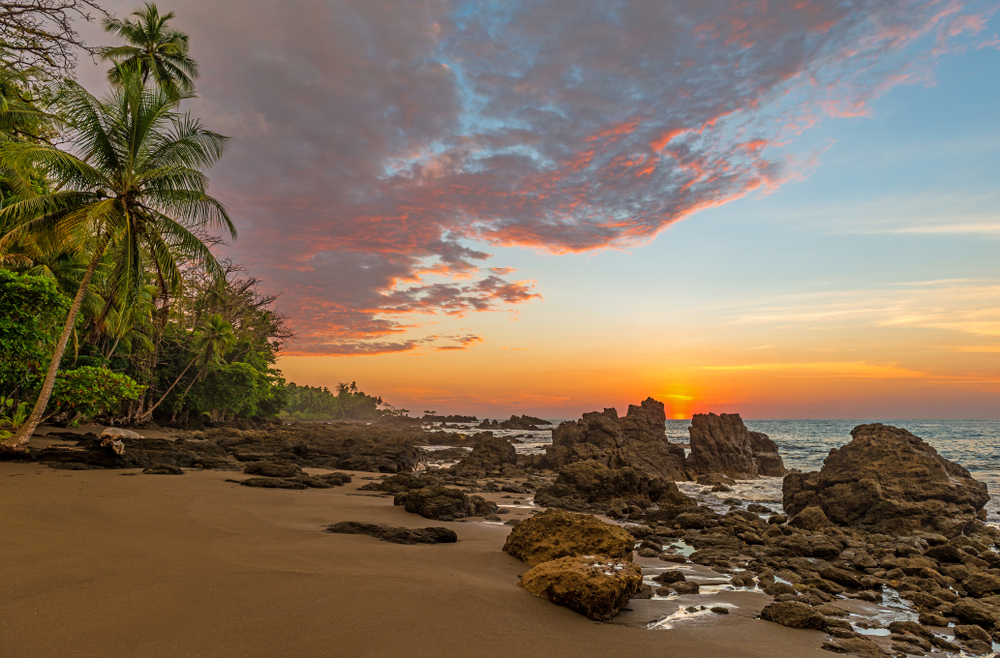

The Nicoya Peninsula in Costa Rica is home to one of the world’s longest-living populations. People in this region enjoy a diet that’s rich in beans, corn, and squash, with a focus on fresh, locally grown foods. They also drink “agua de sapo,” a traditional drink made from lemon and honey, believed to have anti-inflammatory properties. Their culture emphasizes a sense of purpose, with older adults often contributing to their communities through work and mentorship.
Nicoyans also tend to have a positive outlook on life and maintain strong family relationships. Their daily routines include moderate physical activity, like walking, and they avoid the stress associated with modern urban life, contributing to their long, healthy lives. According to Blue Zones, the Nicoya region is recognized as a Blue Zone due to its residents’ high quality of life and longevity. However, recent studies indicate that this longevity advantage is diminishing in newer cohorts.
5. Loma Linda, California, USA
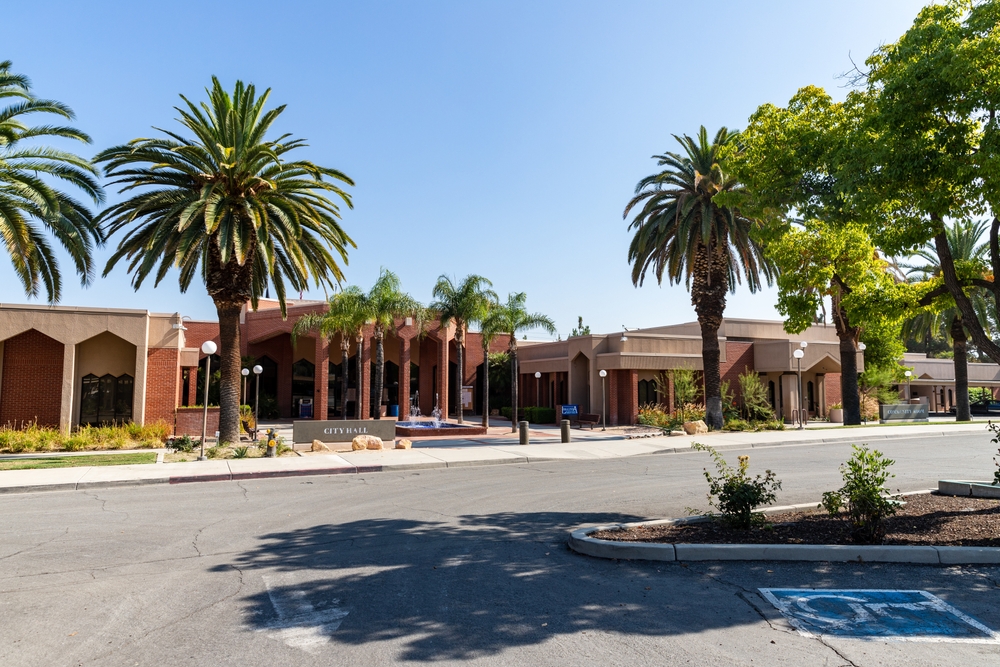

Loma Linda is home to a significant number of Seventh-day Adventists, a religious group known for their long lifespans. A plant-based diet, heavy on fruits, vegetables, nuts, and legumes, is central to their way of life. Adventists also follow the Sabbath, taking one day off per week to rest, which contributes to lower stress levels and a sense of spiritual well-being. Their commitment to physical activity, including daily walks and community events, supports their longevity.
Their strong sense of faith and community provides a sense of purpose and belonging, which plays a significant role in their mental and emotional health. This balanced lifestyle, with a focus on rest, healthy eating, and exercise, has contributed to their remarkable longevity.
6. The Hunza People, Pakistan
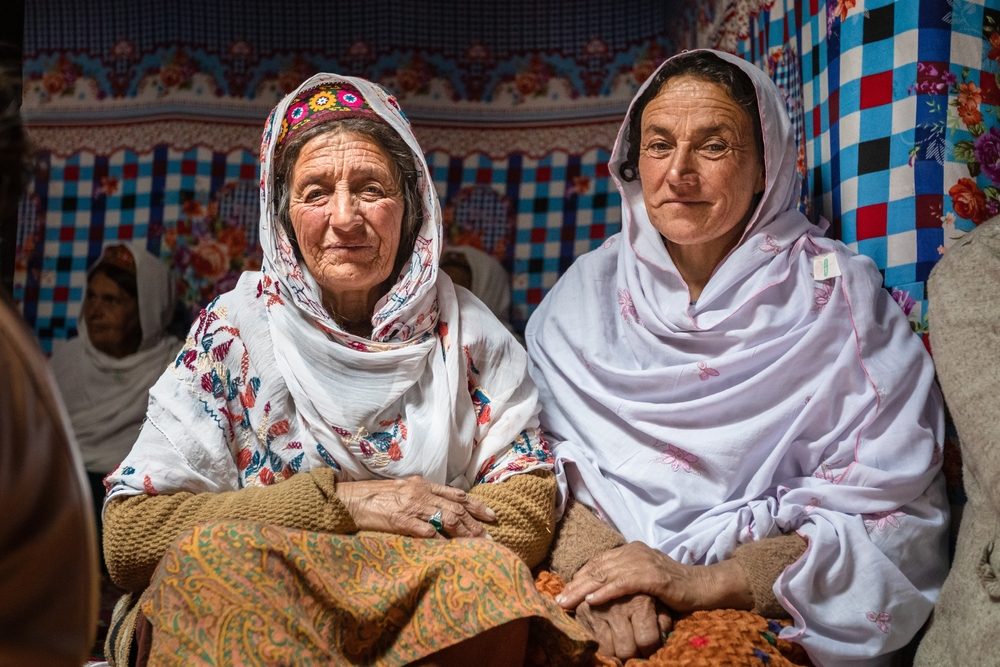

The Hunza people, living in the mountainous regions of northern Pakistan, are often cited as one of the longest-living cultures. Their diet is primarily plant-based, with an abundance of apricots, vegetables, and whole grains. Hunza people are also known for their active lifestyle, climbing hills and hiking daily, which keeps their bodies fit and resilient.
One of the key factors in their longevity is their close connection to nature and a strong sense of community. The Hunza people maintain a positive outlook on life, focusing on gratitude and nurturing strong family bonds, which contribute to their physical and mental health.
7. The Abkhasia Region, Georgia

The Abkhazian people of the Caucasus Mountains in Georgia are known for their longevity, with many living well into their 100s. Their diet is low in meat and rich in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, especially fermented milk. They also consume a lot of wine, which is made locally and consumed in moderation as part of their daily routine.
Their secret to longevity lies in their active lifestyle, with many Abkhazian elders still working on farms well into their 80s and 90s. Strong family values, a tight-knit community, and minimal stress also play significant roles in their long and healthy lives.
8. Bama, China

Bama, a small village in China’s Guangxi province, is home to a large number of centenarians. The diet in Bama is simple, with a heavy emphasis on rice, vegetables, and medicinal herbs. They also consume moderate amounts of fish and lean meats. The people of Bama have a healthy relationship with food, eating in moderation and focusing on balance.
Community and family play an important role in their lives, providing a support system that helps reduce stress. The Bama people also prioritize rest and a slow-paced lifestyle, with many taking naps during the day and enjoying a quiet, peaceful existence.
9. The Aymara People, Bolivia
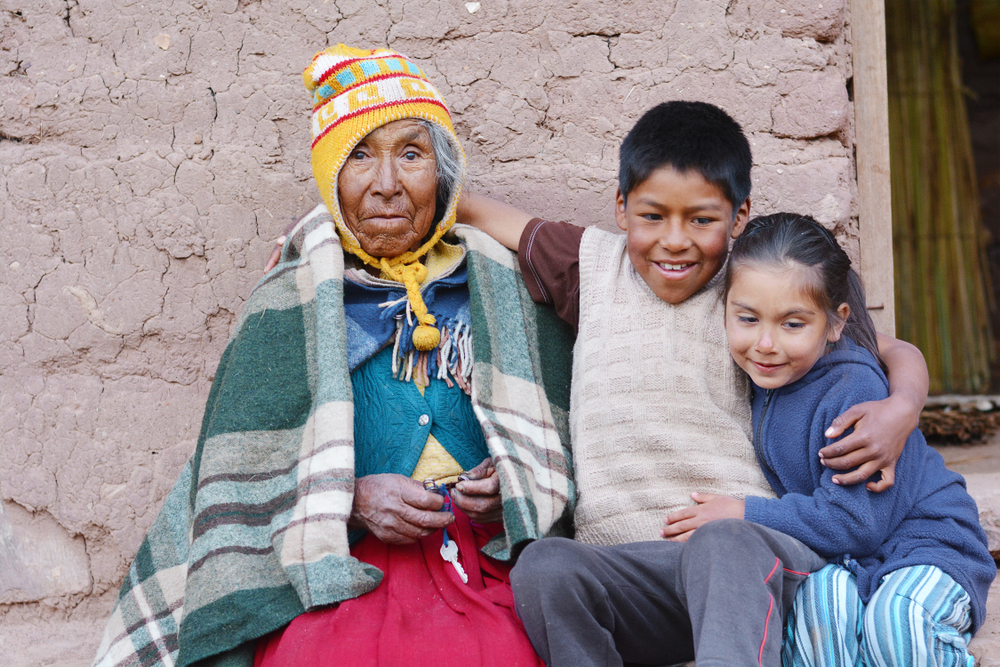

The Aymara people, indigenous to the Andes mountains in Bolivia, are known for their exceptional longevity. Their diet includes quinoa, potatoes, corn, and beans—foods that are rich in nutrients and fiber. The Aymara people also consume herbal teas made from local plants that are believed to support digestion and overall health.
Physical activity is ingrained in their culture, with many Aymara people working in agriculture and walking long distances regularly. Their deep spiritual connection to the land, combined with their diet and lifestyle, is believed to be a significant factor in their long lifespans.
10. Vilcabamba, Ecuador
Vilcabamba, located in the Andes, is often referred to as the “Valley of Longevity” due to the high number of centenarians in the area. The local diet is based on fresh fruits and vegetables, with an emphasis on local herbs, beans, and corn. Vilcabambans also live a relatively stress-free life, with many engaging in farming and outdoor activities well into their later years.
Social support and a strong sense of community are crucial to their longevity. Vilcabambans prioritize family and socializing, which helps reduce isolation and promotes mental health. The clean air, natural surroundings, and low levels of environmental pollution contribute to their overall well-being.
11. The Sherpa People, Nepal
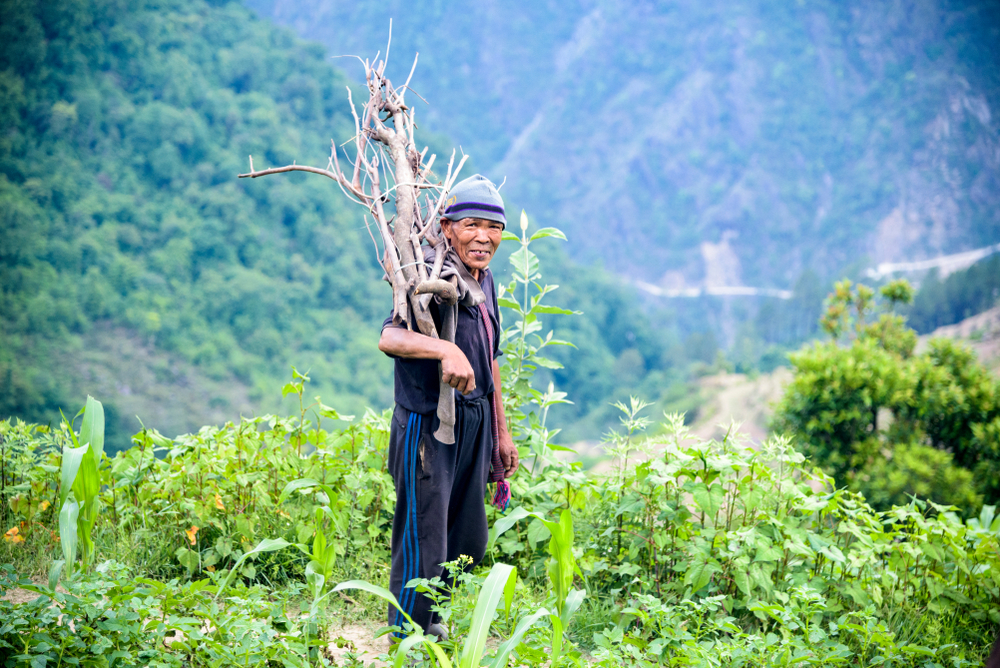

The Sherpa people of Nepal, known for their ability to withstand high altitudes, are renowned for their endurance and longevity. Their diet primarily consists of whole grains, vegetables, and yak butter, providing them with the energy and nutrients needed for their physically demanding lifestyles. Sherpas are also known for their daily physical activity, which includes hiking and trekking in the Himalayan mountains.
The Sherpas’ high level of physical fitness, coupled with their close-knit community and spiritual practices, plays a vital role in their overall health and longevity. Their regular exposure to nature, combined with a simple, active lifestyle, helps them stay fit and mentally strong throughout their lives.
12. The Kurds, Turkey
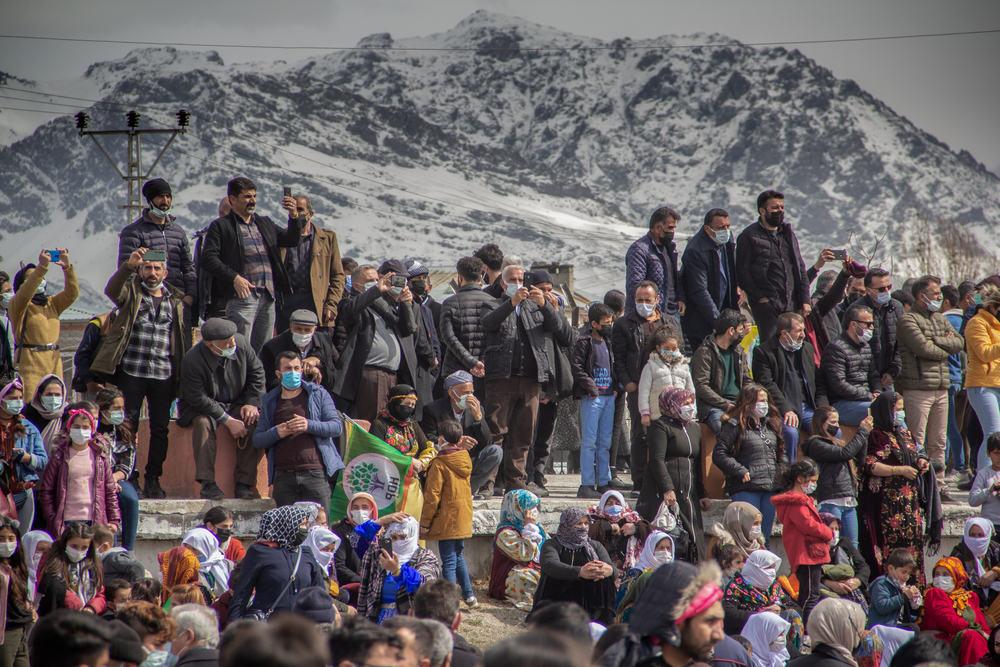

The Kurdish people, particularly in the mountains of Turkey, live long and healthy lives due to a diet rich in vegetables, grains, and fruits. Their diet is mostly plant-based, with a high consumption of legumes, olive oil, and yogurt, which provides probiotics that support gut health. The Kurdish people also engage in daily physical activity, such as farming and walking, which keeps their bodies fit and resilient.
Family and community are incredibly important to the Kurdish people, and they maintain a strong sense of connection to their heritage and the land. This sense of purpose and belonging is essential to their long, healthy lives.
13. The Tsimane People, Bolivia
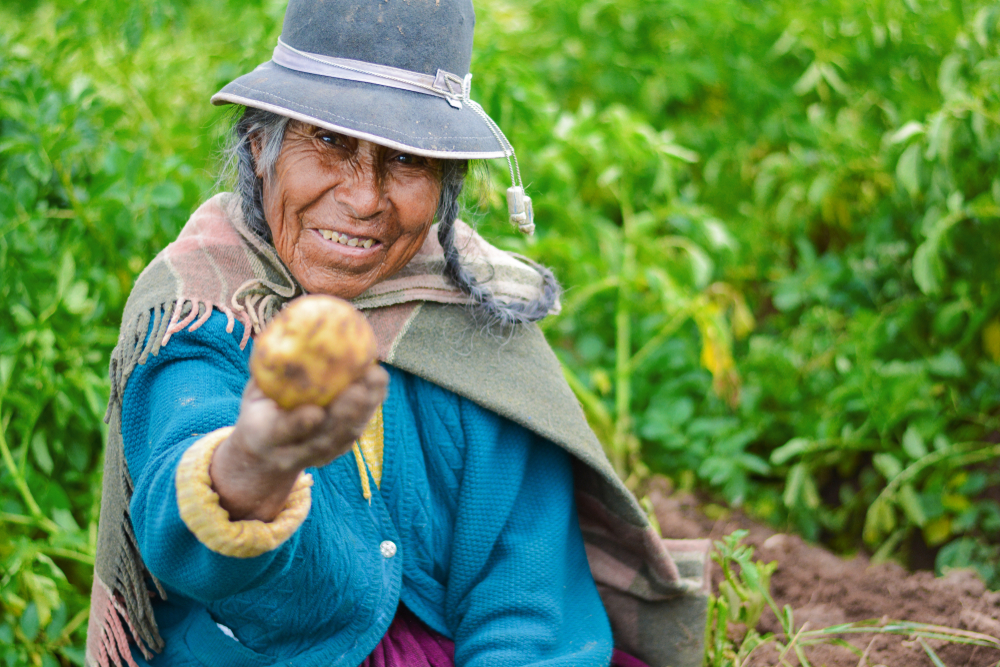

The Tsimane people, living in the Bolivian Amazon, have one of the lowest rates of heart disease in the world, with many living well into their 100s. Their diet is primarily plant-based, with a heavy emphasis on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. The Tsimane people also rely on hunting and fishing, which provides them with lean sources of protein.
Their lifestyle includes a significant amount of physical activity, as they engage in subsistence farming and regularly walk long distances. Their low levels of processed foods, combined with high physical activity and a strong sense of community, contribute to their long and healthy lives.
14. The Hadza People, Tanzania
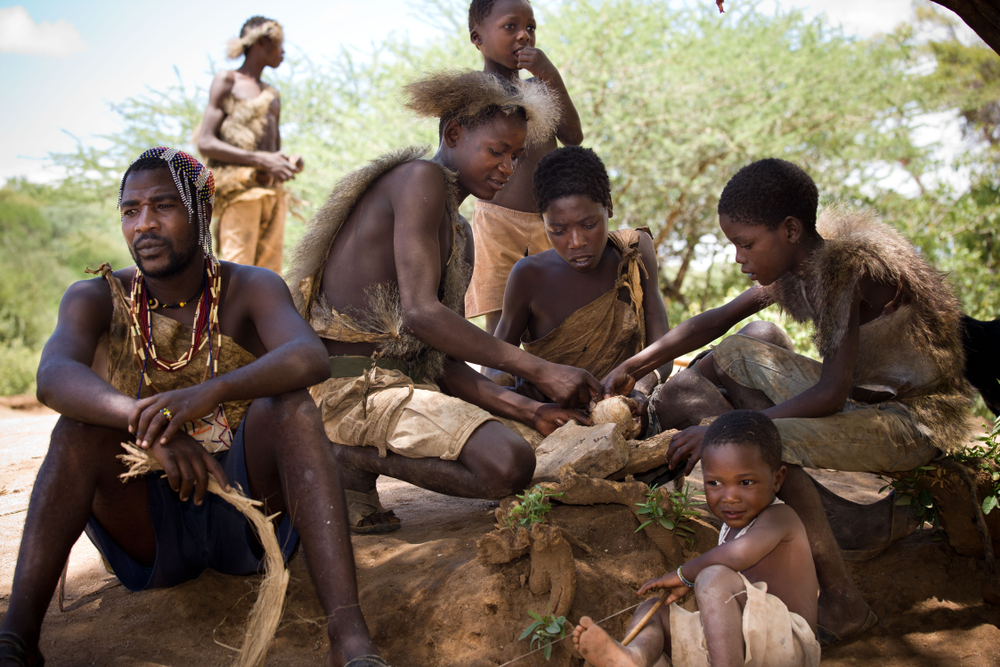

The Hadza people of Tanzania are one of the last remaining hunter-gatherer societies, and their way of life contributes to their longevity. Their diet consists mainly of wild foods such as tubers, berries, honey, and meat, providing them with a nutrient-dense and balanced intake. The Hadza people are physically active, constantly moving, hunting, and gathering, which keeps their bodies strong and resilient.
The Hadza culture also emphasizes strong social bonds, with intergenerational support and deep connections to their community. Their lifestyle, free from modern stressors and processed foods, allows them to maintain good health and longevity.
15. The Maori People, New Zealand
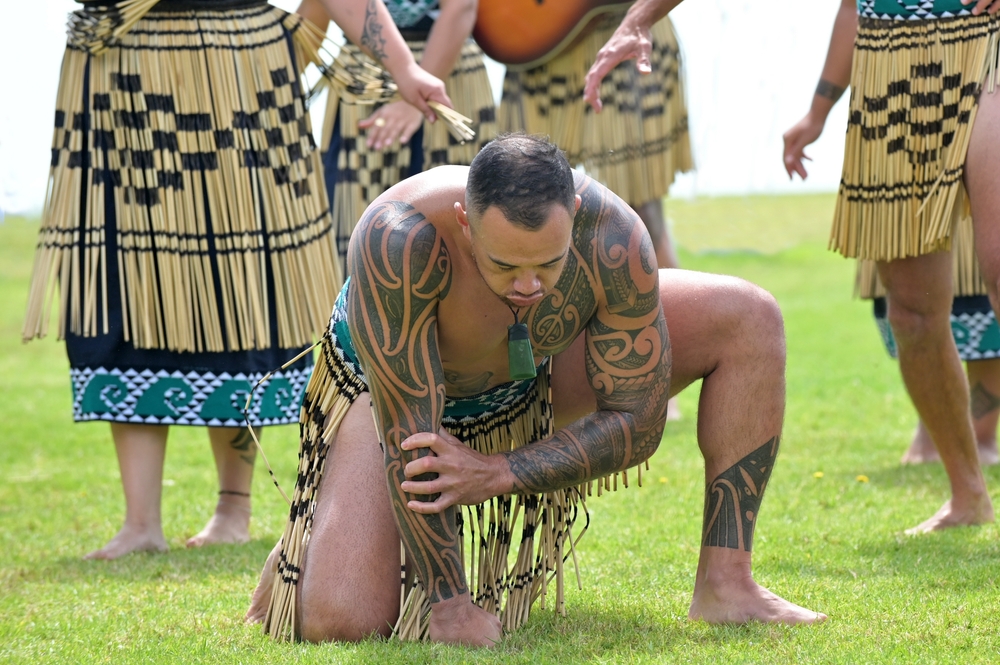

The Maori people of New Zealand have long been known for their cultural practices and resilience, contributing to their longevity. Their traditional diet is based on seafood, root vegetables, and greens, providing essential nutrients and omega-3 fatty acids. Physical activity is also a core part of their culture, with many participating in sports, traditional dances, and outdoor activities that promote cardiovascular health.
Additionally, the Maori people have a deep spiritual connection to the land, which fosters a sense of purpose and community. Their respect for elders and strong social networks play a significant role in their mental and emotional well-being, leading to longer, healthier lives.
Abisola is a communication specialist with a background in language studies and project management. She believes in the power of words to effectively connect with her audience and address their needs. With her strong foundation in both language and project management, she crafts messages that are not only clear and engaging but also aligned with strategic goals. Whether through content creation, storytelling, or communication planning, Abisola uses her expertise to ensure that her messages resonate and deliver lasting value to her audience.


