Ultra-processed foods are everywhere, and while they may be convenient and tasty, they often come with hidden health risks. These foods are designed for long shelf lives and mass consumption, but they can lack essential nutrients and contain ingredients that could be harmful in the long run. Knowing how to spot the red flags can help you make healthier food choices. Here are 15 signs that your food is ultra-processed and devoid of nutrition.
1. The Ingredient List Is Long and Unfamiliar
One of the first red flags that a food is ultra-processed is a long ingredient list filled with names you can’t recognize. These ingredients are often chemicals, preservatives, and artificial additives meant to enhance flavor, texture, or shelf life. According to the Harvard School of Public Health, ultra-processed foods typically contain a mix of ingredients that are not found in whole foods. If you can’t pronounce the majority of the items on the list, chances are it’s not a whole food. Look for foods with simple, recognizable ingredients—anything more complex usually indicates heavy processing.
Ultra-processed foods are engineered to be convenient, but they lack the wholesome qualities of natural ingredients. If you’re seeing additives like artificial sweeteners, colorings, or stabilizers, it’s a clear indication that the food has been altered far beyond its original form. Stick to foods that don’t require a science degree to understand what’s inside them.
2. It’s Packed With Added Sugar
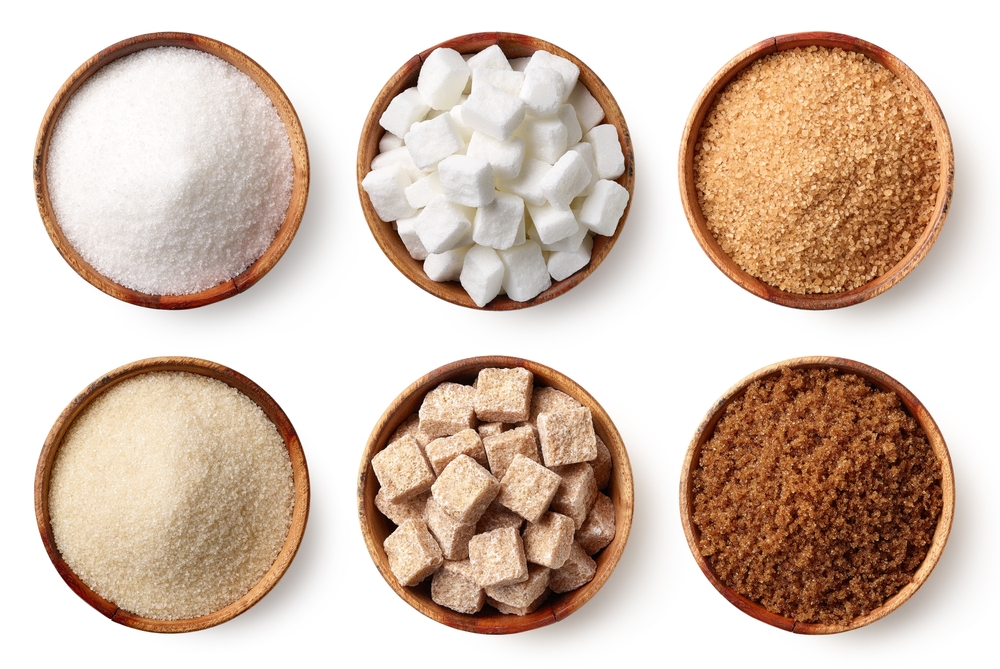

Added sugars are one of the biggest culprits in ultra-processed foods. These sugars are not naturally occurring but are instead added during manufacturing to enhance sweetness and extend shelf life. According to Medical News Today, consuming too much added sugar can lead to weight gain, diabetes, and other health issues over time. When you see “sucrose,” “fructose,” “high-fructose corn syrup,” or other sugar derivatives in the ingredient list, you know that the food is likely ultra-processed.
What’s troubling is that ultra-processed foods can contain sugar in many forms, which can quickly add up without you realizing it. Consuming too much-added sugar may make you feel energetic for a brief moment but will lead to crashes and long-term health concerns. Always check the sugar content on food labels and aim to avoid excessive added sugar in your diet
3. It Has an Artificial Taste or Smell

Ultra-processed foods are often loaded with artificial flavors, colors, and preservatives to make them more appealing and extend their shelf life. According to the World Health Organization, food additives can be derived from various sources and are used to enhance taste and appearance. If you notice that the food has an overly sweet, savory, or unnatural taste, it’s likely packed with synthetic ingredients.
Artificial flavors are commonly added to snacks, drinks, and sweets to mimic the taste of fresh or natural ingredients. If the food tastes more like a science experiment than something straight from nature, it’s probably not offering much in terms of nutrition. Natural foods, by contrast, have vibrant, varied tastes that can’t be replicated by chemicals.
4. It Has an Excessive Amount of Salt

Too much sodium is a common feature of ultra-processed foods. Salt is added not just for flavor but also to preserve food and enhance its texture. According to Houston Methodist, excessive sodium intake can lead to health risks such as high blood pressure and heart disease. If your food tastes unusually salty or you see salt listed early in the ingredients, it’s a warning sign.
Excessive sodium is not just bad for your heart; it can also contribute to bloating, dehydration, and kidney strain. Monitoring your sodium intake is key to maintaining good health, so try to avoid processed foods that are loaded with added salt. Opt for fresh foods that naturally contain lower levels of sodium for a healthier option.
5. It’s Low in Fiber
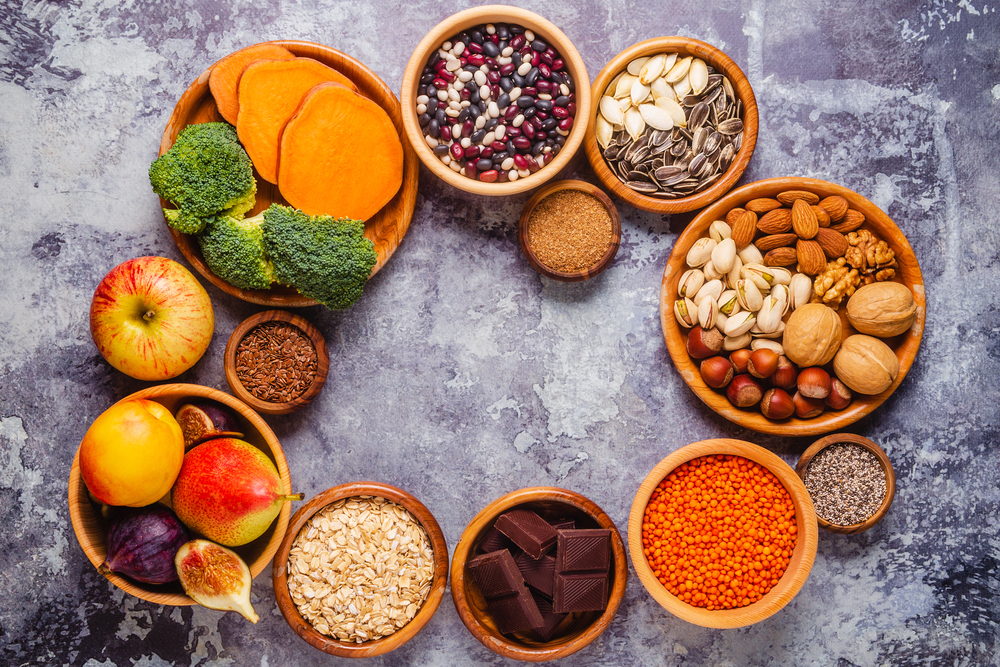

Fiber is essential for digestive health, blood sugar regulation, and overall well-being. However, ultra-processed foods are often stripped of fiber during production. If you look at the nutritional label and notice that your food is low in fiber, it’s likely been heavily processed. Fiber is found in whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and legumes—foods that ultra-processing tends to remove or degrade.
Without sufficient fiber, your digestive system struggles, and you may experience issues like constipation, bloating, and blood sugar imbalances. Many processed snacks and meals contain little to no fiber, leaving you hungry soon after consumption. To keep your digestive health in check, look for foods high in fiber, which naturally helps regulate your system and improve satiety.
6. It Contains Hydrogenated Oils

Hydrogenated oils, also known as trans fats, are a red flag for ultra-processed foods. These fats are chemically altered to stay solid at room temperature and prolong the shelf life of packaged products. Trans fats can increase bad cholesterol (LDL) while lowering good cholesterol (HDL), raising the risk of heart disease and stroke. If you see “partially hydrogenated” or “hydrogenated” oils in the ingredient list, you’re looking at an ultra-processed product.
These unhealthy fats can cause inflammation in the body and contribute to chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes. Although they may provide texture and flavor in processed foods, their long-term impact on health makes them a major concern. Stick to whole, natural fats like those from avocados, olive oil, and nuts, which support better health.
7. It’s High in Unnecessary Additives and Preservatives

Preservatives, stabilizers, and emulsifiers are commonly added to ultra-processed foods to keep them fresh longer or maintain a certain texture. While these additives may not necessarily make the food “unsafe” in the short term, they do little for your health. Ingredients like BHA, BHT, and sodium benzoate have been linked to various health concerns, including cancer and hormone disruption, when consumed in large amounts over time.
While these additives help preserve foods and enhance shelf life, they are far removed from the nutrients your body truly needs. Fresh, unprocessed foods contain vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that these additives cannot replace. Be cautious of processed foods loaded with unnecessary chemicals and preservatives, as they may be doing more harm than good.
8. The Packaging Promises “Low Fat” or “Diet” Benefits

Many ultra-processed foods market themselves as “low fat,” “diet,” or “fat-free” to attract health-conscious consumers. However, these labels often signal that the food has been stripped of beneficial nutrients like healthy fats and is instead loaded with sugar or artificial ingredients to compensate for flavor. In reality, consuming “diet” foods often leads to overeating, as they may not satisfy your hunger.
Foods marketed as low-fat are often processed to the point of lacking essential nutrients. Healthy fats are crucial for brain function, energy, and absorption of vitamins, so avoiding them in favor of overly processed alternatives can be detrimental. Choose whole foods that naturally contain the right balance of healthy fats for better nutrition.
9. It’s Made With Refined Grains

Refined grains are often a primary component in ultra-processed foods. Unlike whole grains, refined grains have been stripped of their bran and germ during processing, removing much of their fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Common examples include white bread, white rice, and many baked goods. These foods are quickly digested and can cause spikes in blood sugar levels.
Consuming too many refined grains may contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and other metabolic problems. Foods made with whole grains, on the other hand, are packed with fiber and nutrients that help regulate blood sugar and promote satiety. Look for products made with whole grains to ensure you’re getting more nutrition with your meals.
10. It’s High in Calories With Little Nutritional Value

Many ultra-processed foods are packed with calories but offer little to no nutritional benefit. These foods often contain empty calories from sugar, refined grains, and unhealthy fats, leaving you feeling unsatisfied and craving more. Despite the high-calorie content, your body isn’t getting the nutrients it needs to thrive, which can lead to deficiencies and long-term health issues.
Eating ultra-processed foods regularly can contribute to weight gain and poor health, as they lack the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants found in whole foods. Choose foods that provide lasting energy and nutrients, so you’re not just filling up on empty calories that harm your health in the long run.
11. It Has a Long Shelf Life

One of the hallmarks of ultra-processed foods is their long shelf life. Foods that can sit on a shelf for months or even years without spoiling are often loaded with preservatives and artificial ingredients. While convenient, these foods are typically far removed from their natural, nutritious state and offer minimal health benefits.
Natural foods, such as fruits and vegetables, have a much shorter shelf life because they’re perishable. When food can last for a long time, it’s usually an indication that it’s been processed beyond recognition. Opt for fresh, perishable foods whenever possible to ensure that you’re getting the most nutrients out of your meals.
12. It’s Low in Protein
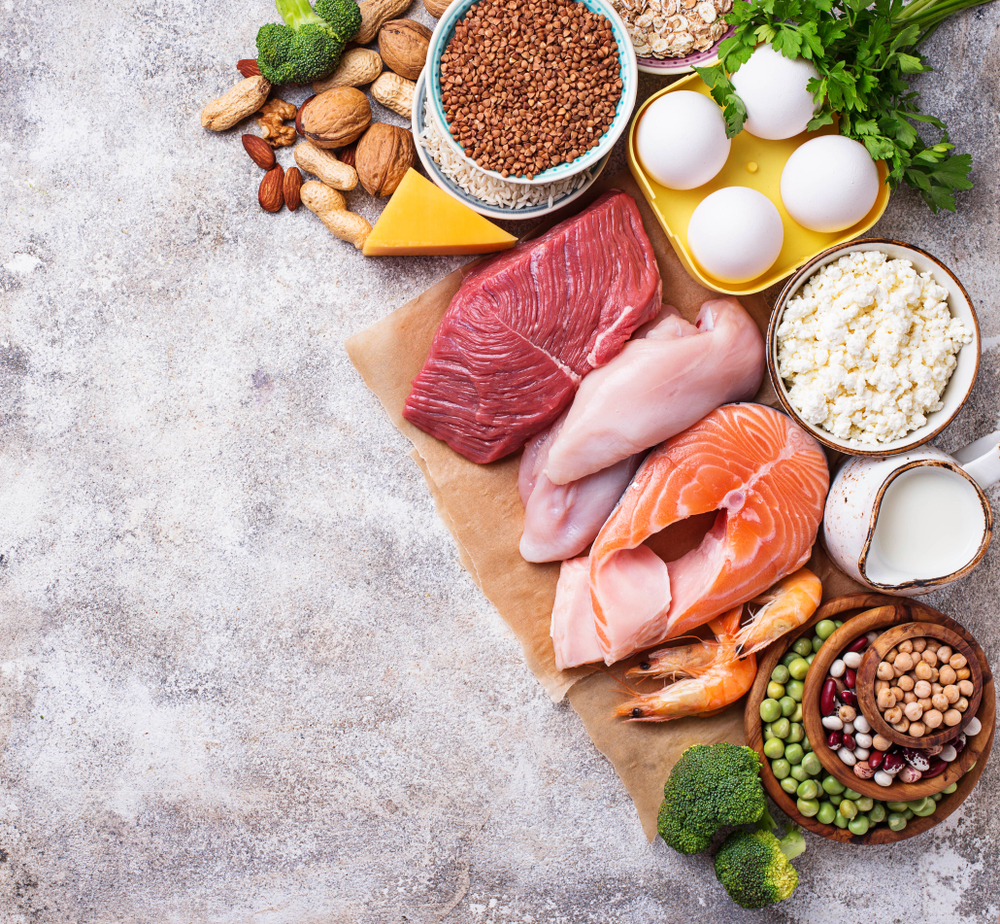

Protein is an essential nutrient for muscle repair, immune function, and overall health. Ultra-processed foods, however, tend to be low in protein and high in sugars, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates. When you don’t get enough protein from your diet, you may experience fatigue, muscle loss, and a weakened immune system.
High-quality protein sources like lean meats, beans, legumes, and nuts provide your body with the necessary building blocks for health. If you’re eating processed snacks that are low in protein, you might feel hungry again soon after eating. Choose foods that naturally provide a good amount of protein to support your body’s needs and maintain long-term health.
13. It’s Overly Sweetened With Artificial Sweeteners

Ultra-processed foods often contain artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, or saccharin to replace sugar and make the product “diet-friendly.” These sweeteners may seem like a healthier option, but they can still affect your body in harmful ways. Studies have shown that artificial sweeteners can lead to cravings for sweeter foods and disrupt gut health.
Despite their low-calorie nature, artificial sweeteners may hurt your metabolism and blood sugar regulation. They also don’t satisfy hunger in the same way that whole foods do, often leaving you wanting more. Stick to natural sources of sweetness, like fruits, and avoid heavily processed foods that rely on artificial sweeteners for taste.
14. It’s High in Trans Fats
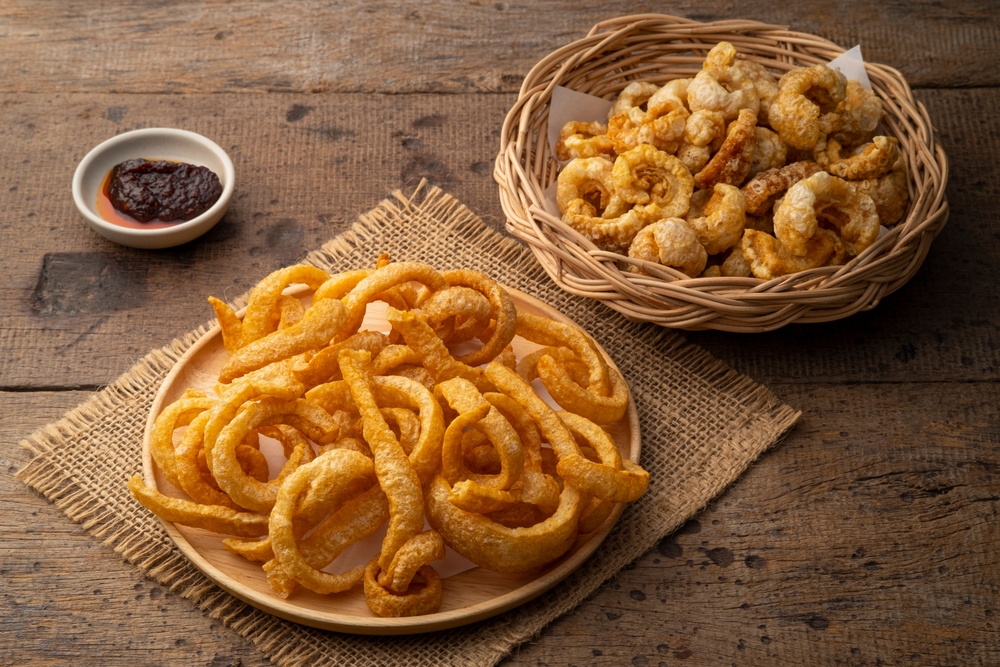

Trans fats are unhealthy fats that have been linked to increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. They’re often found in ultra-processed foods like pastries, fried foods, and packaged snacks. Trans fats are created through a process called hydrogenation, which turns liquid oils into solids, improving the texture and shelf life of foods.
While they extend the shelf life of products, trans fats contribute to inflammation in the body and negatively affect cholesterol levels. Be sure to check the label for trans fats or partially hydrogenated oils, which are the key indicators of these harmful fats. Prioritize whole, natural fats for a healthier lifestyle, avoiding processed foods that are loaded with trans fats.
15. It’s Heavily Advertised as “Convenient” or “Quick”
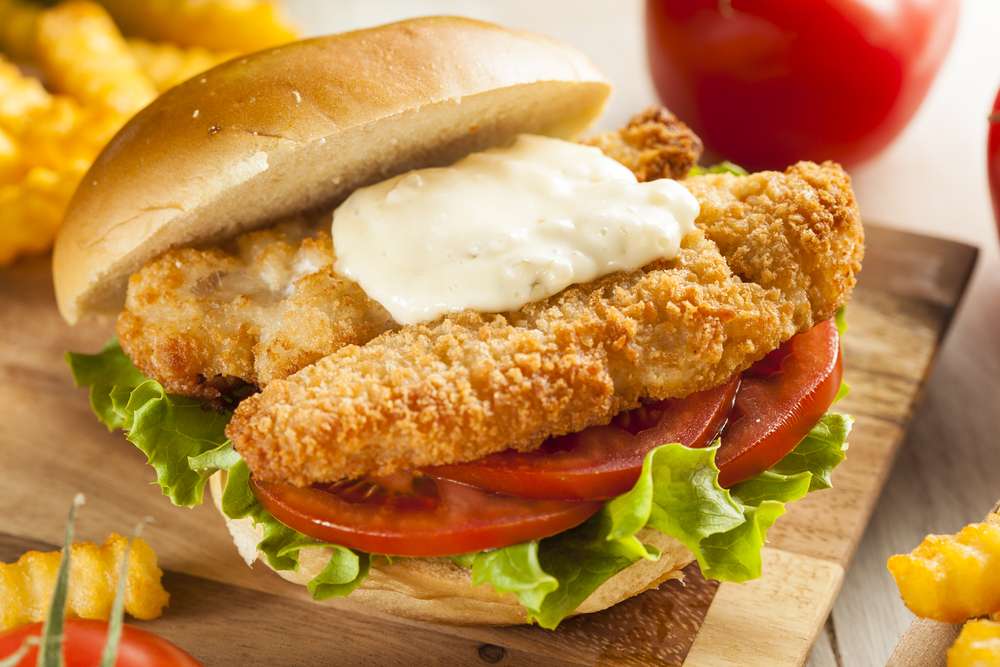

Ultra-processed foods often come with flashy advertisements touting their convenience or quick preparation time. While these foods may be time-saving, they often sacrifice nutritional value for convenience. The faster and easier a food is to prepare, the more likely it has undergone significant processing and lacks the nutrients your body needs.
While convenience is tempting, it’s important to remember that fast food and pre-packaged meals rarely offer the health benefits of fresh, whole foods. Instead of opting for highly processed, easy-to-prepare foods, try meal prepping or cooking simple, fresh meals that provide more nutrition and support overall well-being. Your health is worth the extra effort.
Natasha is a seasoned lifestyle journalist and editor based in New York City. Originally from Sydney, during a stellar two-decade career, she has reported on the latest lifestyle news and trends for major media brands including Elle and Grazia.


