The idea of reversing the aging process has long been a topic of science fiction, but recent breakthroughs suggest that aging backwards might not be as impossible as we once thought. While it may sound far-fetched, some scientists believe that advanced research and technology can slow down or even reverse the aging process in certain ways. In this article, we’ll explore 15 reasons why aging backwards could be possible, according to cutting-edge science.
1. Telomere Lengthening

Telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, naturally shorten as we age, leading to cell death and the signs of aging. However, scientists have discovered that it may be possible to lengthen telomeres through gene therapy, potentially reversing the effects of aging at the cellular level. According to Frontiers in Genetics, centenarians exhibit unique telomere dynamics, maintaining longer telomeres and higher telomerase activity than younger cohorts. By restoring telomere length, cells could continue dividing and functioning optimally for much longer. This breakthrough could be the key to slowing or reversing the biological clock.
Some studies have shown that telomere lengthening could reverse aging symptoms in certain cells, such as skin and blood cells. If this technology becomes widely available, it could pave the way for anti-aging treatments that could extend lifespan and improve quality of life. While it’s still in the early stages of development, telomere manipulation has shown promising potential in reversing cellular aging.
2. Senolytics: Targeting Senescent Cells
Senescent cells are damaged cells that no longer divide or function properly, and they accumulate as we age. These dysfunctional cells release harmful substances that can contribute to age-related diseases. According to Frontiers in Aging, senolytics enhance immune cell function and tissue repair by suppressing the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Researchers have discovered a class of drugs called senolytics that can target and destroy these senescent cells, promoting healthier aging. By clearing out these cells, the body can regenerate and repair itself more effectively, leading to a reversal of aging-related conditions.
Senolytic therapies have been shown to improve the health and function of organs like the heart, kidneys, and liver. In animal models, clearing senescent cells has led to improvements in physical fitness and reduced signs of aging. If these treatments prove successful in humans, they could play a major role in reversing the biological effects of aging and enhancing longevity. Clinical trials are exploring senolytics like dasatinib and quercetin for age-related diseases, with early results showing reduced inflammation and improved physical resilience.
3. Stem Cell Therapy

Stem cells are remarkable for their ability to regenerate damaged tissue and create new cells. According to the Chinese Medical Journal, stem cells like neural and mesenchymal stem cells improve outcomes in age-related conditions such as macular degeneration and osteoarthritis. Scientists are now exploring how stem cell therapy could be used to reverse aging by replenishing tissues that have worn down over time. By introducing new, youthful stem cells into aging organs and tissues, it may be possible to repair damage caused by the natural aging process.
Recent advancements in stem cell therapy have shown promising results in treating age-related diseases. Researchers are also working on methods to rejuvenate stem cells themselves, ensuring they remain effective for longer. If stem cell therapy can be optimized, it could become a powerful tool in reversing aging and extending healthy lifespan. While SC therapies face delivery and safety hurdles, their ability to repair damaged organs positions them as a cornerstone of anti-aging research.
4. Caloric Restriction And Fasting

Caloric restriction, or reducing calorie intake without malnutrition, has been shown to extend lifespan in several animal studies. According to Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, dietary restriction with adequate nutrition is the gold standard for delaying aging and extending healthspan and lifespan in diverse species. Fasting, especially intermittent fasting, has similar effects on the body, promoting autophagy—the process of cleaning out damaged cells and regenerating new ones. These practices may slow down aging and increase longevity by optimizing cellular maintenance and function.
Studies in humans are still ongoing, but there is evidence to suggest that caloric restriction and fasting can lead to better health markers, including improved heart health and reduced inflammation. While it’s not a magic bullet for aging, incorporating caloric restriction or intermittent fasting into one’s lifestyle could help delay the onset of age-related diseases and potentially reverse some of the effects of aging. These dietary interventions optimize metabolic health and resilience, offering practical strategies to delay age-related decline.
5. Reprogramming Cells With Yamanaka Factors

Yamanaka factors, a set of four genes, have been discovered to have the ability to reprogram adult cells into pluripotent stem cells, which are capable of becoming any cell type in the body. This reprogramming process has shown great promise in reversing cellular aging and restoring youthful function. In animal models, the use of Yamanaka factors has led to the reversal of age-related diseases and the rejuvenation of tissues like the heart and skin.
The idea of using gene therapy to reprogram aging cells could be a game-changer in regenerative medicine. By turning back the cellular clock, scientists could potentially reverse aging at a genetic level, rejuvenating tissues and organs that have deteriorated over time. Although much of the research is still in the experimental stages, Yamanaka factors represent a fascinating avenue for potential anti-aging therapies.
6. Mitochondrial Rejuvenation
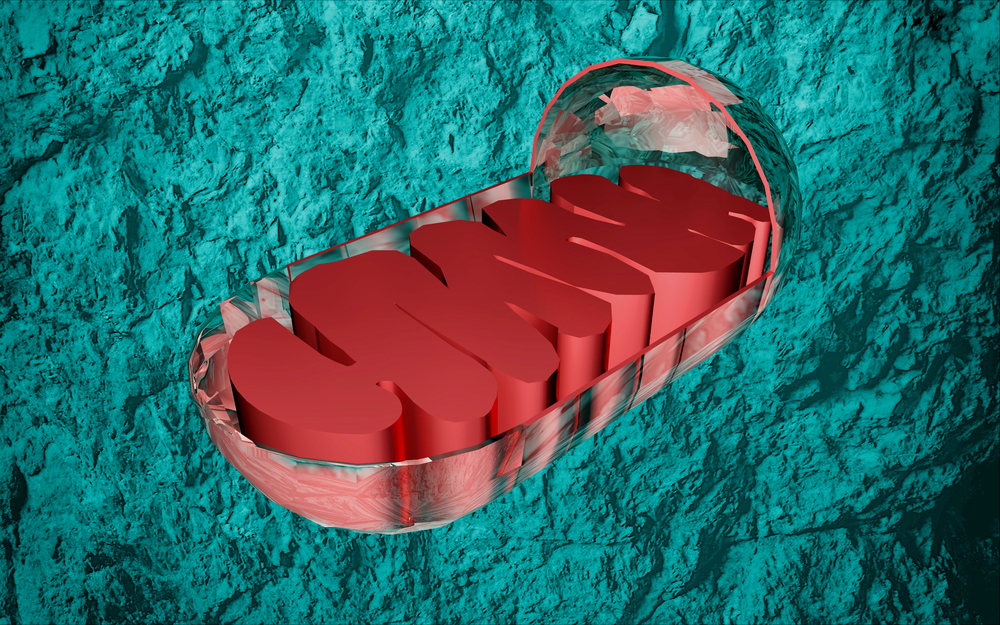

Mitochondria, the powerhouses of our cells, become less efficient with age, leading to reduced energy production and cellular dysfunction. Researchers are exploring ways to rejuvenate mitochondria and restore their function, potentially reversing many age-related health issues. By enhancing mitochondrial function, cells can produce more energy, which can improve overall health, muscle strength, and cognitive function.
One approach being studied is the use of compounds like NAD+ boosters, which have been shown to improve mitochondrial health and extend lifespan in animal models. Restoring mitochondrial function could help reverse age-related decline in energy levels, making it a key strategy for slowing aging. If successful, mitochondrial rejuvenation could lead to a wide range of benefits, from improved vitality to better brain health.
7. Epigenetic Reprogramming

Epigenetic changes, which affect how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence, play a significant role in aging. Over time, these epigenetic changes can cause cells to function less efficiently and contribute to age-related diseases. However, scientists are now investigating ways to reverse epigenetic changes, effectively “reprogramming” the body back to a younger, healthier state. Epigenetic reprogramming could allow the body to regenerate cells and tissues, potentially reversing the effects of aging.
In animal studies, scientists have successfully reversed age-related epigenetic changes, leading to improvements in tissue health and function. By targeting the epigenetic factors that control gene expression, researchers hope to develop therapies that can rejuvenate the body at the genetic level. If these methods can be applied to humans, they may be able to slow or reverse the aging process by restoring youthful epigenetic patterns.
8. Hormonal Therapy
As we age, hormone levels naturally decline, leading to a variety of age-related symptoms such as fatigue, muscle loss, and cognitive decline. Some scientists believe that restoring youthful hormone levels through hormone replacement therapy (HRT) could help reverse some of these effects. By supplementing hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and growth hormone, the body may regain vitality and improve physical and mental health.
While HRT has been used for years to treat menopause symptoms, recent studies suggest it could have broader anti-aging effects, including enhanced muscle mass, improved energy, and better skin health. However, the long-term safety of HRT remains a topic of debate, and researchers are working to determine the best protocols for its use. If done safely and effectively, hormone therapy could help reverse certain aging signs and contribute to overall well-being.
9. The Role Of Anti-Aging Molecules

Scientists are continuously discovering molecules that have the potential to combat aging at the cellular level. For example, resveratrol, a compound found in red wine, has been shown to activate sirtuins—proteins that help repair DNA and regulate aging. Other compounds like metformin and rapamycin have also shown promise in extending lifespan by influencing cellular processes that govern aging. These anti-aging molecules may hold the key to reversing some of the biological processes associated with aging.
While much of the research is still in its early stages, these molecules offer hope for developing treatments that could slow down or even reverse aging. Many of these compounds are being studied for their potential to extend life and prevent age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s and cancer. As science advances, we may see these molecules play a significant role in aging therapies, giving us a chance to age backward.
10. Reducing Inflammation

Chronic inflammation is a key driver of many age-related diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s. Researchers are focusing on ways to reduce inflammation to slow down the aging process and promote healthier aging. By using anti-inflammatory drugs, lifestyle changes like diet and exercise, or other targeted therapies, it may be possible to reduce the inflammatory response in the body and reverse some of the damage caused by inflammation over time.
One promising approach is the use of natural compounds like curcumin (found in turmeric) and omega-3 fatty acids, both of which have anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds have shown potential in reducing markers of inflammation and improving overall health. By targeting inflammation, scientists hope to delay the onset of age-related diseases and potentially reverse some of the effects of aging.
11. The Power Of Sleep

Sleep is one of the most underrated factors when it comes to aging. Quality sleep promotes cellular repair and rejuvenation, and a lack of it accelerates aging. Researchers are increasingly recognizing that sleep not only helps us recover but also plays a critical role in maintaining our longevity. By improving sleep quality, it may be possible to reduce the effects of aging and promote better health over time.
Sleep therapies, such as improving sleep hygiene, reducing blue light exposure, and using sleep aids when necessary, have shown promise in enhancing the restorative effects of sleep. By ensuring the body gets proper rest, we can slow down aging at the cellular level and rejuvenate the body’s systems. Optimizing sleep could be a simple but powerful tool in reversing some of the effects of aging.
12. The Role Of Antioxidants
Antioxidants, found in a variety of fruits and vegetables, have long been praised for their ability to fight free radicals—unstable molecules that cause oxidative stress and accelerate aging. Free radicals can damage cells, proteins, and DNA, leading to age-related diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s. By consuming antioxidant-rich foods or taking supplements, it may be possible to protect the body from oxidative damage and slow down the aging process.
Research has shown that antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and flavonoids can help neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation in the body. This, in turn, may help prevent or reverse some of the cellular damage associated with aging. With the right combination of antioxidants, it might be possible to protect the body from the aging process and extend healthy years of life.
13. Gene Editing And CRISPR Technology

CRISPR technology has revolutionized the field of genetics by allowing scientists to edit genes with incredible precision. Researchers are exploring how gene editing could be used to repair or modify genes associated with aging. For example, genes that control the repair of DNA or the maintenance of telomeres could potentially be edited to restore youthfulness and reverse age-related damage.
Although gene editing is still in the early stages, the potential for reversing aging is enormous. With the ability to precisely target and alter specific genes, scientists may one day be able to eliminate genetic mutations that contribute to aging. This groundbreaking technology offers hope for a future where aging is no longer inevitable, and it’s possible to biologically reverse the clock.
14. The Impact Of Social Connections

Maintaining strong social connections has been shown to improve overall health and longevity. Studies have found that people with close relationships tend to live longer, healthier lives. Social interactions can reduce stress, improve mental health, and even promote physical well-being by encouraging healthier behaviors. By nurturing social bonds, it’s possible to slow down the aging process and extend quality years of life.
Engaging with friends, family, and community not only boosts emotional well-being but also supports cognitive function and physical health. Social connection can also enhance the effectiveness of other anti-aging strategies, such as exercise and stress management. By prioritizing relationships, individuals may be able to reverse the mental and emotional aging process.
15. Advances In Artificial Intelligence And Biotechnology

Artificial intelligence and biotechnology are rapidly advancing, bringing us closer to the possibility of aging backwards. AI is being used to analyze vast amounts of data to identify new drugs and therapies that could slow or reverse aging. Biotechnology is advancing in areas such as tissue regeneration, gene therapy, and regenerative medicine, all of which have the potential to rejuvenate the body and extend lifespan.
These technologies could help create personalized treatments that target the specific biological processes of aging. As AI and biotechnology continue to evolve, they may unlock new ways to intervene in the aging process and reverse the physical and mental effects of growing older. The future of aging might be far more promising than we ever imagined.
Natasha is a seasoned lifestyle journalist and editor based in New York City. Originally from Sydney, during a stellar two-decade career, she has reported on the latest lifestyle news and trends for major media brands including Elle and Grazia.


