Have you been feeling unusually fatigued, anxious, or experiencing an uptick in allergy symptoms? While these conditions are often thought to be caused by stress, diet, or lifestyle, they could also be linked to the changing climate. As global temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, the environment around us has a direct impact on our physical and mental health. In this article, we explore 14 reasons why your allergies, anxiety, and fatigue might be climate-related.
1. Higher Pollen Levels

As temperatures rise due to climate change, pollen seasons are becoming longer and more intense. This increase in pollen exposure can lead to more severe allergy symptoms such as sneezing, itchy eyes, and nasal congestion. Climate change affects the timing of plant blooming and the amount of pollen released into the air, exacerbating seasonal allergies. For many people, this means that the spring and fall allergy seasons are getting harder to manage.
What’s particularly concerning is that longer exposure to high pollen levels can cause chronic inflammation in the airways. This can lead to a worsening of respiratory conditions like asthma. According to PMC, longer pollen seasons caused by climate change are increasing allergy prevalence and severity worldwide. People who have never had severe allergy symptoms may find themselves suddenly struggling, and those with existing conditions may experience more frequent flare-ups.
2. Increased Air Pollution

Air quality is one of the most significant factors affecting both physical and mental health. Climate change contributes to higher levels of air pollution, particularly in urban areas. This pollution includes pollutants like ozone and particulate matter, which can trigger respiratory problems and exacerbate allergies. Poor air quality can also contribute to anxiety and fatigue, as the body works harder to process toxins in the environment.
Research has shown that exposure to high levels of air pollution can lead to increased stress, irritability, and even depression. According to Psychiatry.org, air pollution has been linked to neuroinflammation, which affects mental health by increasing risks for depression and anxiety. Those who are sensitive to pollution may experience worsened symptoms like fatigue and difficulty breathing.
3. Extreme Heat Waves
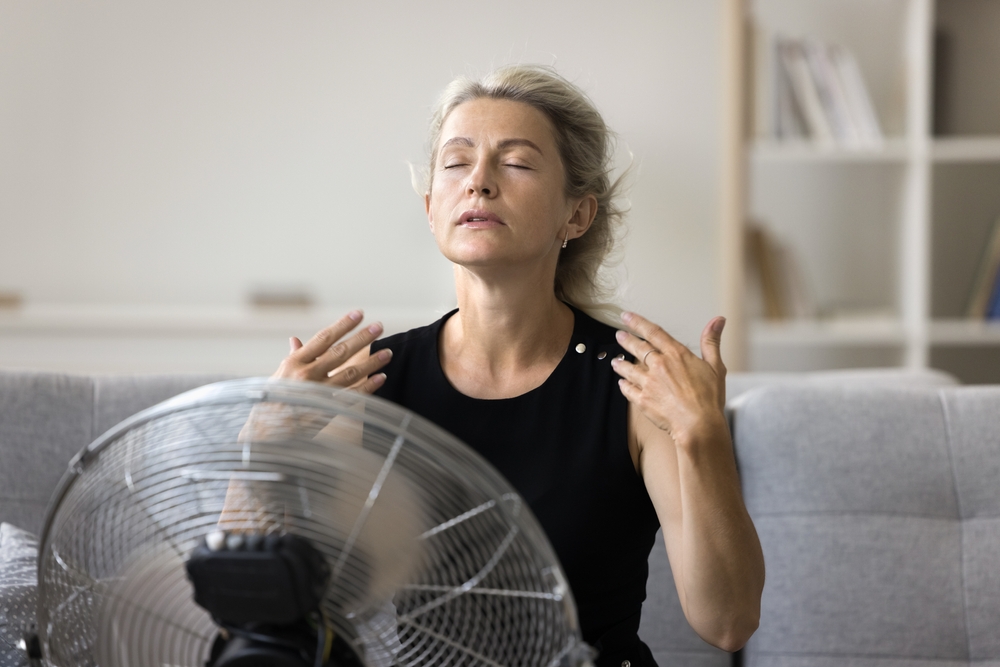

Heat waves, which are becoming more frequent due to global warming, are not only physically exhausting but also mentally taxing. Extended periods of extreme heat can lead to dehydration, fatigue, and difficulty sleeping. These physical symptoms can then trigger or worsen mental health issues like anxiety and depression. As your body struggles to cope with excessive heat, your energy levels may drop significantly, leaving you feeling drained and irritable.
Heatwaves can also make it harder to maintain a routine, with many people retreating indoors due to the oppressive weather. This disruption to daily life can add to feelings of isolation and anxiety. According to WHO, prolonged heat exposure increases stress hormones like cortisol, which contribute to anxiety and fatigue.
4. Changes In Seasonal Patterns

Climate change is causing unpredictable shifts in weather patterns, leading to an increase in unpredictable weather events such as storms, floods, and extreme temperatures. These abrupt changes can trigger stress and anxiety, as our bodies and minds are not always prepared for these shifts. Additionally, the uncertainty caused by climate-induced weather events can lead to chronic feelings of anxiety and worry about the future.
These weather disruptions not only affect mental health but can also interfere with sleep patterns, causing fatigue and stress. According to PMC, unpredictable seasonal patterns caused by climate change amplify feelings of unease while affecting physical energy levels through disrupted routines and heightened stress responses.
5. Increased Humidity
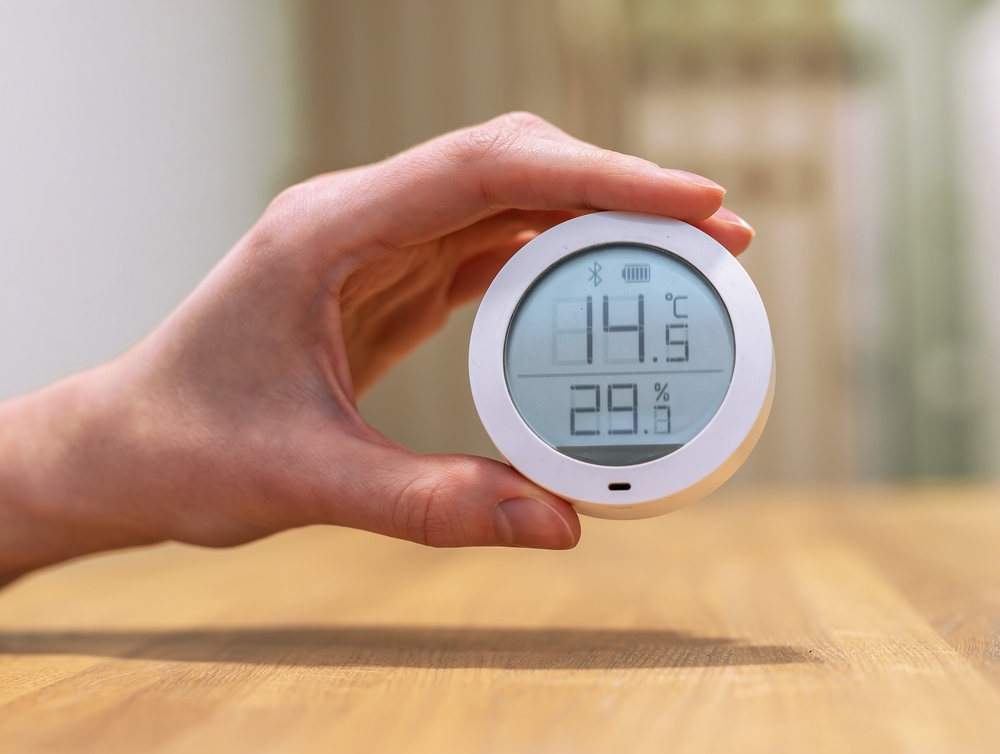

Humidity levels have been rising as the climate changes, and this can lead to a variety of health issues. High humidity can make it difficult to breathe, exacerbate asthma, and lead to an increase in mold and dust mites, which can trigger allergies. Furthermore, the discomfort of high humidity can make people feel sluggish and mentally fatigued, reducing overall productivity and well-being.
The impact of humidity on mental health is often underestimated. The constant physical discomfort of high humidity can increase irritability and frustration, contributing to mental exhaustion. Over time, this chronic discomfort can lead to heightened anxiety levels, particularly in those who are already predisposed to stress. The oppressive nature of humid weather contributes to feelings of fatigue and unease, making it harder to focus or feel energized.
6. Reduced Sleep Quality Due To Weather Changes
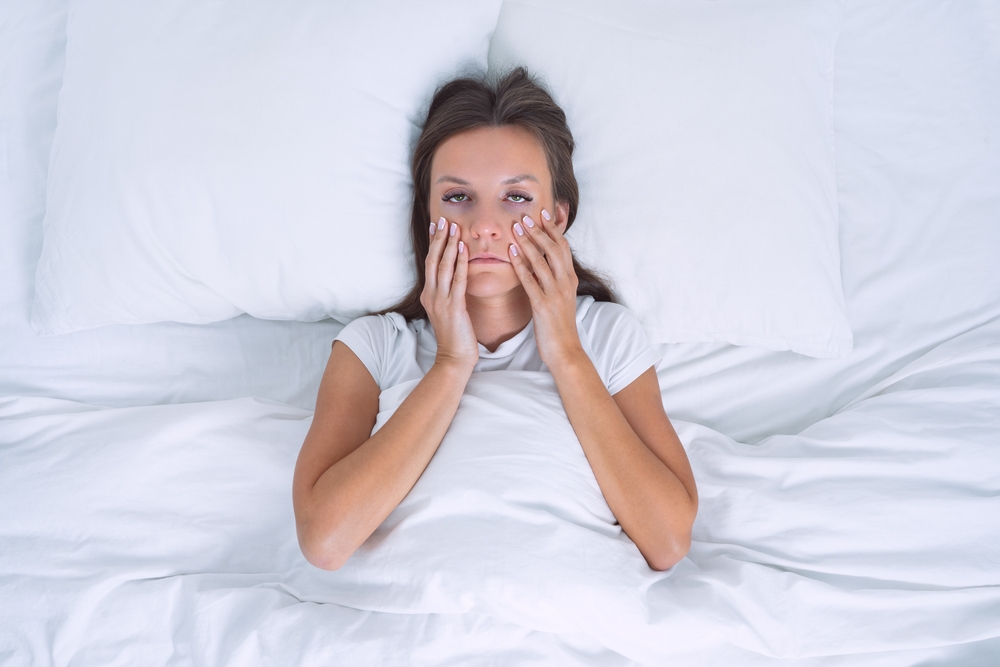

Changes in temperature, humidity, and weather patterns can disrupt sleep quality, leading to fatigue and irritability. As the climate warms, more people report difficulty sleeping, whether due to higher nighttime temperatures or excessive humidity. Poor sleep leads to a lack of restorative rest, which can result in a tired and anxious mind, affecting both mental and physical health.
Inadequate sleep is a well-known contributor to anxiety and stress. When you’re sleep-deprived, your body produces higher levels of stress hormones, making it even harder to relax and recover. Additionally, a lack of quality sleep leads to cognitive impairments, such as poor concentration and irritability, which only add to the anxiety and fatigue you might be feeling. Climate-related disruptions to sleep patterns create a vicious cycle that affects both body and mind.
7. Allergic Reactions To New Plant Species
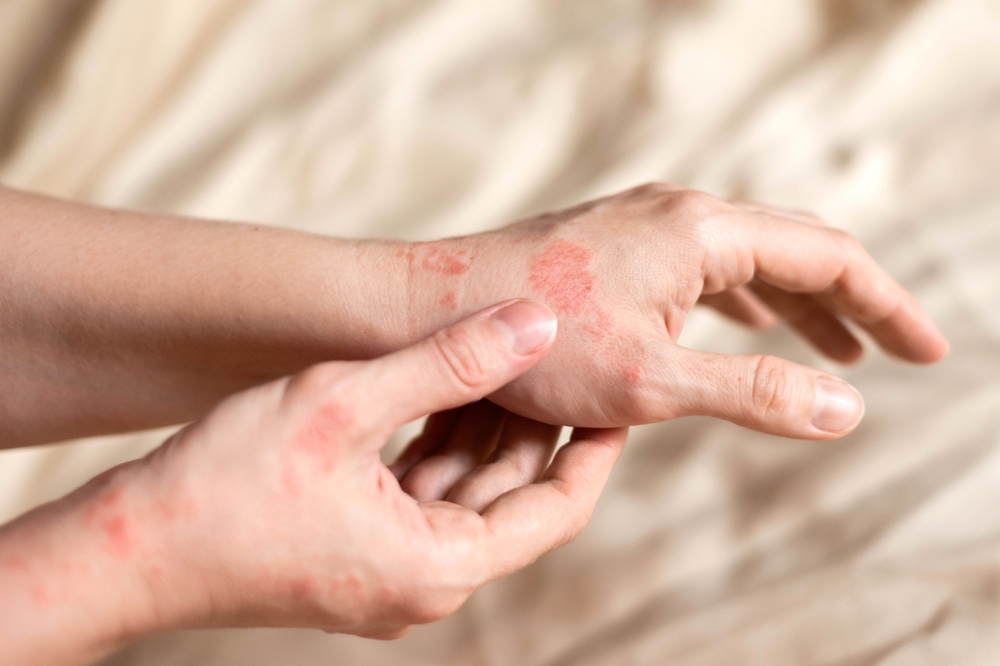

As climate change causes ecosystems to shift, new plant species are emerging in different regions. These plants may produce different types of pollen or allergens, which can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. The expansion of certain plants, like ragweed, is a direct result of warmer temperatures, making allergy symptoms worse and affecting respiratory health.
These new allergens can make it harder for people to manage their symptoms, leading to increased exposure to triggers they may not have experienced before. As these plants thrive in a changing climate, those with pre-existing allergies may face new challenges. The increase in allergens in the air can contribute to respiratory fatigue and worsen anxiety for those who are struggling with constant allergy flare-ups. The unpredictable nature of new allergens adds another layer of stress and discomfort to an already challenging situation.
8. Increased Stress From Natural Disasters
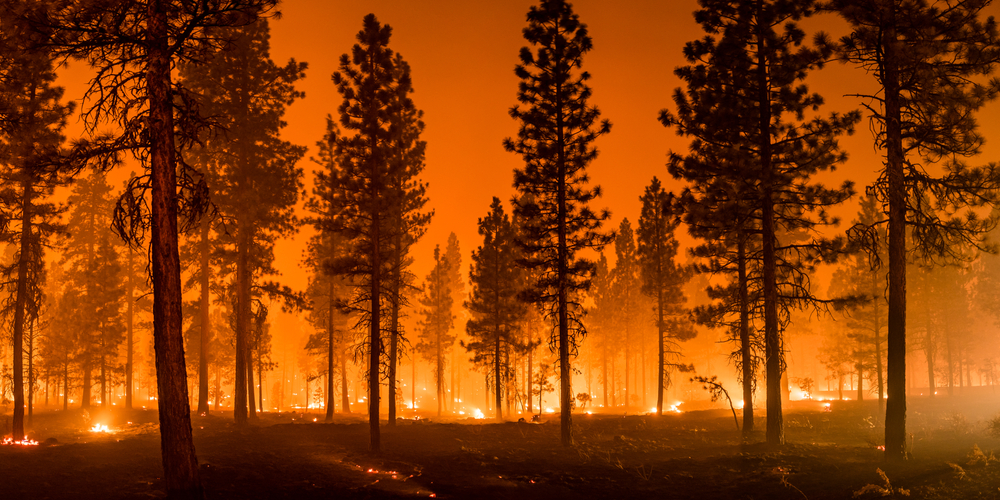

Natural disasters, including hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, are becoming more frequent and severe due to climate change. The trauma and uncertainty caused by these events can lead to significant emotional distress, anxiety, and long-term mental health problems. For individuals affected by these disasters, the stress of recovery and rebuilding can contribute to exhaustion and anxiety, making it harder to regain a sense of normalcy.
The fear and unpredictability of natural disasters also increase anxiety levels, as people worry about future events. This persistent state of alertness and concern for safety can lead to chronic fatigue and sleep disturbances. In the aftermath of a disaster, people may struggle with feelings of loss, anxiety about the future, and a sense of helplessness. The long-term psychological impact of these climate-related events can contribute to ongoing stress and fatigue.
9. Dehydration Due To Increased Heat
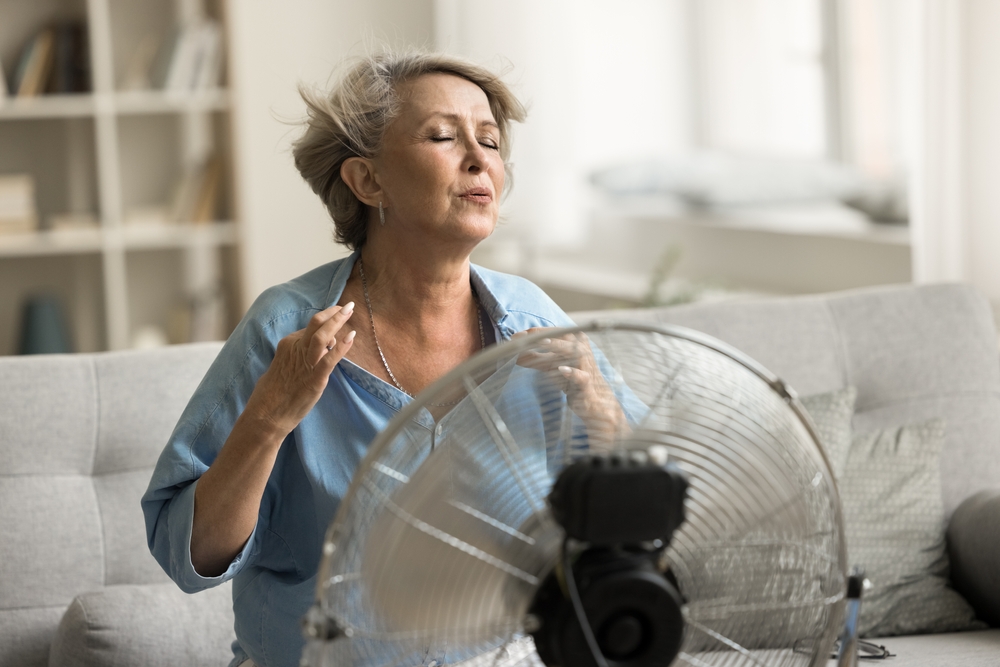

Increased temperatures and heat waves are leading to higher rates of dehydration. Dehydration, even in its mild forms, can lead to fatigue, headaches, and dizziness. These physical symptoms can also trigger feelings of anxiety, as the body struggles to maintain proper hydration levels in extreme heat. The combination of dehydration and heat-related exhaustion can leave you feeling drained both physically and mentally.
Dehydration affects cognitive function, making it harder to focus and leading to irritability and anxiety. Chronic dehydration can have long-term effects on overall health, contributing to feelings of fatigue and low energy. As climate-related heat events become more frequent, it’s important to stay hydrated and protect against the physical and mental consequences of dehydration. Being proactive about hydration is key to maintaining energy levels and mental clarity in the face of rising temperatures.
10. Changes In Food Availability And Nutrition

Climate change is impacting agriculture and food systems around the world, leading to changes in food availability and nutritional quality. Poor nutrition can lead to fatigue, anxiety, and a weakened immune system. Climate-related disruptions to food supply chains may result in nutrient deficiencies, which can directly affect mental and physical health.
For example, reduced access to fresh produce or nutrient-rich foods can lead to imbalances that contribute to anxiety and fatigue. In particular, a lack of vitamins and minerals like vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and iron can exacerbate feelings of exhaustion and mental stress. The stress of food insecurity or the inability to access healthy foods can also contribute to mental health challenges. The impacts of climate on food systems have a ripple effect on overall well-being, influencing both body and mind.
11. Increased Incidence Of Vector-Borne Diseases

Climate change has led to a rise in diseases transmitted by insects, such as mosquitoes and ticks. These diseases, including malaria, dengue, and Lyme disease, can cause fatigue, fever, and joint pain. The constant threat of vector-borne diseases adds stress and anxiety, as people worry about exposure and the long-term health effects of these illnesses.
In addition to the physical symptoms of these diseases, the anxiety around contracting them can contribute to mental health problems. The fear of potential outbreaks or the constant need for vigilance can increase levels of chronic stress. Fatigue is also a common symptom of many vector-borne illnesses, making it harder for people to recover both physically and mentally. Climate change is causing the spread of these diseases to new regions, increasing the overall burden on public health.
12. Disruption Of Mental Health Services Due To Climate Events

Climate-related events, such as floods, hurricanes, and wildfires, can disrupt access to mental health services. These disruptions leave individuals without the support they need to manage stress, anxiety, or other mental health issues. When mental health resources are limited or unavailable due to climate-related disasters, people are forced to cope on their own, leading to increased anxiety and fatigue.
In some cases, the trauma of experiencing a climate event can overwhelm individuals, leaving them with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or other long-term mental health issues. This lack of support creates a compounding effect, where the physical and emotional stress of climate events leads to lasting mental health challenges. Increased awareness and access to mental health services are crucial in addressing the mental toll of climate change.
13. Reduced Sunlight Exposure

Climate change can lead to periods of more overcast skies, storms, and extreme weather, reducing overall sunlight exposure. Sunlight is essential for maintaining healthy levels of vitamin D, which plays a crucial role in mood regulation and energy levels. Reduced exposure to sunlight can contribute to feelings of fatigue, depression, and anxiety, making it harder to maintain mental and physical health.
Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to a higher incidence of depression and fatigue. As climate change impacts weather patterns and sunlight availability, it’s important to take steps to maintain adequate vitamin D levels, such as through supplementation or spending time outdoors when possible. Ensuring that the body gets enough sunlight is essential for overall well-being, especially during times of climate-related disruption.
14. Changes In Water Quality
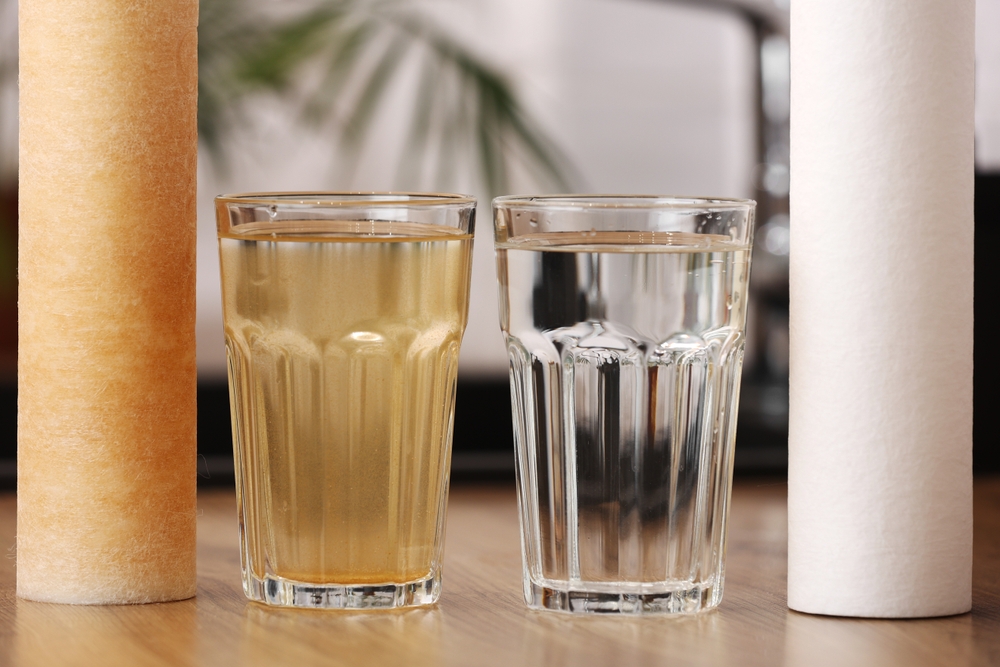

Climate change has altered water systems, leading to changes in water quality and availability. Droughts, floods, and changes in water temperature can all affect water safety, leading to contamination and shortages. Poor water quality can cause dehydration, fatigue, and gastrointestinal issues, which may further contribute to overall health deterioration.
The stress of dealing with water scarcity or unsafe water can also lead to anxiety and emotional exhaustion. For people who live in areas where water contamination is a growing concern, this issue is particularly relevant. Ensuring access to clean and safe water is essential for maintaining both physical and mental health, especially in areas where climate change is impacting water resources.
Abisola is a communication specialist with a background in language studies and project management. She believes in the power of words to effectively connect with her audience and address their needs. With her strong foundation in both language and project management, she crafts messages that are not only clear and engaging but also aligned with strategic goals. Whether through content creation, storytelling, or communication planning, Abisola uses her expertise to ensure that her messages resonate and deliver lasting value to her audience.


