The supplement industry is booming, promising everything from better sleep to weight loss, improved memory, and even longer life. With billions of dollars spent annually, it’s no wonder we’re drawn to the allure of quick fixes in a bottle. However, not all supplements are created equal. Many of them are overhyped, under-researched, or completely ineffective. Here are 12 supplements that claim to boost your health but may be secretly useless—or even a waste of money.
1. Fat Burners

Fat-burning supplements are heavily marketed as a way to shed pounds quickly, but most are loaded with caffeine and stimulants that offer temporary boosts in metabolism at best. Long-term weight loss is better achieved through diet and exercise rather than relying on potentially harmful and ineffective pills.
2. Antioxidant Supplements (Vitamin C, E, and Beta-Carotene)

While antioxidants are crucial for fighting free radicals, getting them in supplement form isn’t the miracle it’s often portrayed to be. Studies have shown that high doses of antioxidant supplements may not reduce disease risk and, in some cases, can even be harmful, particularly beta-carotene supplements in smokers.
3. Collagen Supplements
Collagen supplements promise glowing skin, strong nails, and youthful joints, but they’re not as miraculous as they seem. Your body breaks down collagen into amino acids during digestion, which means you’re not necessarily getting collagen directly where it’s needed. Eating a protein-rich diet may provide the same benefits at a fraction of the cost.
4. Multivitamins
Multivitamins are one of the most popular supplements on the market, but research shows they may not live up to the hype. For most people who eat a balanced diet, multivitamins offer little to no additional health benefits. Excess vitamins and minerals are simply flushed out of your body, making them an expensive habit without much payoff.
5. Detox Teas and Supplements

Your liver and kidneys already detoxify your body naturally, yet detox supplements claim to do what your body is already doing for free. There’s little scientific evidence to back up detox products, and some may even contain harmful laxatives that can cause dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.
6. Probiotics in Capsule Form

While probiotics can be beneficial, not all probiotic supplements are effective. Many capsules fail to deliver live bacteria to your gut due to stomach acid breakdown. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut are often better options for improving gut health.
7. Glucosamine and Chondroitin
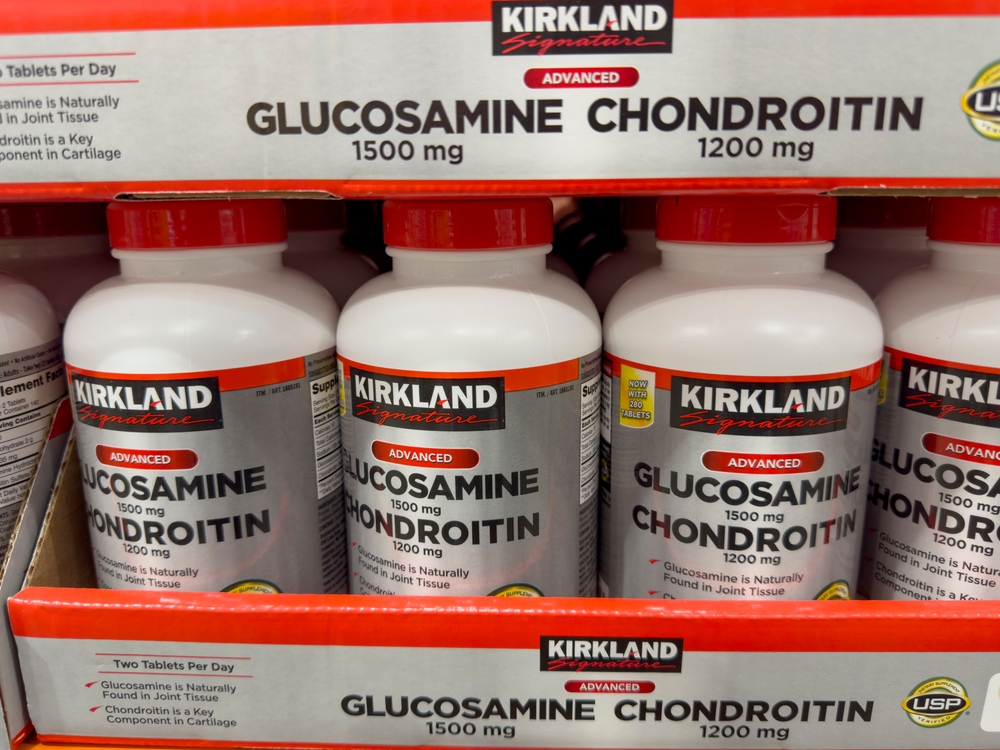
These supplements are marketed as joint saviors, especially for arthritis sufferers. However, large-scale studies have shown mixed results, with little evidence that they consistently reduce pain or improve joint function beyond a placebo effect.
8. Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)

BCAAs are popular among fitness enthusiasts as muscle-building supplements, but they’re often unnecessary if you’re consuming enough protein in your diet. Complete protein sources like chicken, eggs, or beans already provide all the amino acids your body needs for muscle repair and growth.
9. Homeopathic Remedies

Homeopathic supplements are based on highly diluted substances and claim to stimulate the body’s healing processes. However, the scientific consensus is clear: there’s no evidence that homeopathy works beyond a placebo effect. Skip these and look for evidence-based treatments instead.
10. Memory Boosters (Ginkgo Biloba)

Ginkgo biloba is often marketed as a brain booster that improves memory and prevents cognitive decline. Unfortunately, multiple studies have shown it has no significant impact on memory or the progression of dementia. Save your money for proven brain health practices like exercise and balanced nutrition.
11. Biotin for Hair and Nails

Biotin supplements are widely popular for promoting hair and nail growth, but they’re unnecessary unless you have a biotin deficiency, which is rare. Most people get enough biotin through their diet, and adding more won’t speed up hair or nail growth.
12. Vitamin D “Mega Doses”

While vitamin D is essential for bone health and immunity, mega doses are unnecessary and can even be harmful. Excessive vitamin D can lead to toxicity, causing symptoms like nausea, kidney damage, and high calcium levels. A moderate dose or safe sun exposure is usually sufficient.
Supplements are tempting because they promise an easy path to better health, but many fall far short of their claims. Instead of wasting money on these 12 overrated products, focus on eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.



