Many people unknowingly engage in daily habits that gradually shorten their lifespan. While some of these behaviors may seem harmless, science has proven that they contribute to long-term health problems. From poor dietary choices to excessive screen time, these habits slowly take a toll on physical and mental well-being. The problem is that their effects aren’t immediate, making them easy to overlook. However, over time, they increase the risk of chronic diseases, cognitive decline, and even premature aging. Here are 12 common daily habits that may be quietly taking years off your life—and what you can do to stop them.
1. Sitting for Long Periods Without Movement
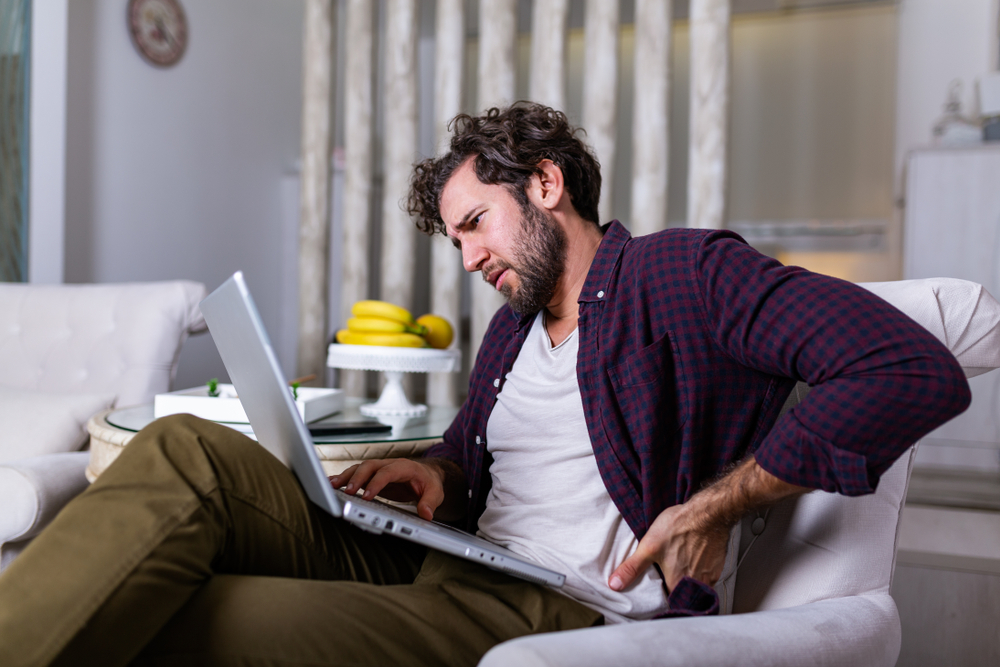

Sedentary behavior is one of the biggest yet most overlooked risks to longevity. Research has linked prolonged sitting to increased risks of heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and even early death. Sitting for extended periods slows metabolism, reduces circulation, and leads to muscle deterioration. Even regular exercise doesn’t fully counteract the negative effects of excessive sitting. The body thrives on movement, and a lack of it accelerates aging at a cellular level.
Incorporating more activity into daily routines can counteract these effects. Standing up, stretching, or walking for a few minutes every hour improves circulation and prevents stiffness. Using a standing desk, taking walking meetings, or simply pacing during phone calls helps keep the body engaged. Even small changes, like parking farther from a destination or using stairs instead of elevators, can make a difference. Prioritizing movement throughout the day is key to maintaining long-term health. According to Healthline, sitting for long periods can lead to numerous health issues, including increased risks of heart disease and diabetes.
2. Sleeping Too Little or Too Much

Inconsistent or poor-quality sleep has been directly linked to a shorter lifespan. Sleep is essential for cellular repair, immune function, and mental clarity. Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, obesity, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s. On the other hand, sleeping too much—especially more than nine hours per night—has also been associated with an increased risk of premature death. Striking the right balance is crucial for overall health.
Establishing a consistent sleep routine improves both quality and longevity. Avoiding blue light from screens before bed, reducing caffeine intake, and maintaining a comfortable sleep environment can enhance sleep quality. Experts recommend 7-9 hours of sleep per night for most adults. Prioritizing rest allows the body to repair itself, reduces inflammation, and improves cognitive function. Sleep isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity for a longer, healthier life. According to CNN, following good sleep habits can significantly increase life expectancy.
3. Eating Too Much Processed Food

Processed foods are filled with preservatives, artificial ingredients, and unhealthy fats that contribute to chronic diseases. Studies have linked excessive consumption of processed food to higher risks of obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. These foods often lack essential nutrients while being high in sugars, salt, and unhealthy oils that trigger inflammation. Inflammation is a key factor in aging and is linked to numerous health conditions that reduce life expectancy.
Shifting to a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods can significantly improve longevity. Fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provide essential nutrients that support the body’s natural functions. Reducing reliance on processed snacks, sugary drinks, and fast food lowers the risk of disease and boosts overall energy levels. While occasional indulgence is fine, making whole foods the foundation of a diet promotes long-term health. According to Medical News Today, high consumption of ultra-processed foods is associated with accelerated biological aging.
4. Chronic Stress and Unmanaged Anxiety

Long-term stress takes a serious toll on both physical and mental health. Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which can lead to high blood pressure, weakened immunity, and accelerated aging. Studies have shown that prolonged stress contributes to inflammation, increasing the risk of heart disease, depression, and cognitive decline. Many people experience stress daily without realizing its long-term effects.
Practicing stress management techniques can help counteract these negative effects. Mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity all reduce cortisol levels. Engaging in hobbies, socializing, and spending time in nature also help the body relax and recover from stress. Setting boundaries at work and prioritizing mental well-being improves both emotional and physical health. Stress is inevitable; however, how you manage it determines its impact on your lifespan. According to Mayo Clinic, effective stress management techniques are vital for maintaining overall health.
5. Drinking Sugary Beverages Daily

Sugary drinks like soda, fruit juices, and energy drinks are some of the leading causes of obesity, diabetes, and metabolic diseases. Studies have found that excessive sugar consumption contributes to chronic inflammation and increases the risk of heart disease. Liquid sugar is absorbed rapidly into the bloodstream, causing insulin spikes that over time lead to insulin resistance. This process accelerates aging and increases the risk of premature death.
Switching to healthier beverage choices can significantly improve health. Drinking water, herbal teas, and naturally flavored sparkling water helps keep the body hydrated without the harmful effects of sugar. Reducing sugary drink intake lowers the risk of diabetes, weight gain, and other metabolic disorders. Small daily changes, such as choosing water over soda, can add years to your life. Hydration should support the body’s health, not harm it.
6. Constant Exposure to Screens and Blue Light

Excessive screen time—whether from phones, computers, or TVs—negatively impacts sleep, vision, and mental health. Prolonged exposure to blue light disrupts melatonin production, leading to poor sleep quality. Studies have linked excessive screen time to increased risks of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. The habit of mindlessly scrolling through social media also contributes to stress and decreased attention spans.
Reducing screen time, especially before bed, can significantly improve overall well-being. Taking regular breaks from screens, using blue light filters, and engaging in offline activities helps protect eye health and mental focus. Setting screen-free times during meals or before bedtime promotes better sleep and emotional balance. While technology is essential in modern life, excessive use should be controlled for long-term health.
7. Skipping Strength Training
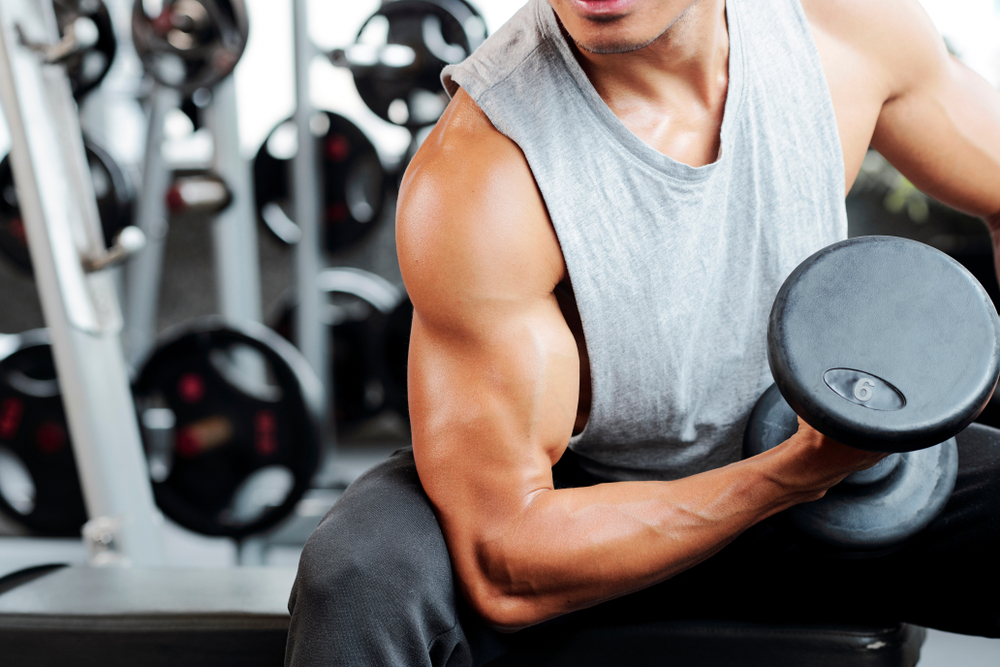

Many people focus on cardio but neglect strength training, which is essential for longevity. Studies show that maintaining muscle mass as you age reduces the risk of frailty, osteoporosis, and metabolic diseases. Strength training improves bone density, supports joint health, and enhances metabolism. A lack of muscle-building exercise leads to faster muscle loss and an increased risk of injury in later years.
Incorporating resistance training into weekly routines helps maintain strength and function. Lifting weights, doing bodyweight exercises, or practicing resistance band workouts all contribute to long-term health. Even just two to three sessions per week can significantly improve muscle retention and overall longevity. Strength isn’t just for athletes—it’s necessary for maintaining independence and vitality as you age.
8. Neglecting Mental Stimulation and Lifelong Learning

Failing to challenge the brain regularly can contribute to cognitive decline and increase the risk of dementia. Studies show that engaging in mentally stimulating activities strengthens neural connections, reducing the likelihood of memory loss and cognitive impairment. Many people fall into repetitive routines without learning new skills or engaging in problem-solving tasks. Over time, this lack of stimulation causes brain function to deteriorate faster than it should. Mental inactivity accelerates aging just as much as physical inactivity.
Incorporating lifelong learning into daily life helps keep the brain sharp and resilient. Reading, learning a new language, solving puzzles, or engaging in creative hobbies all promote brain health. Studies suggest that people who remain intellectually engaged have a lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. Social interaction, such as discussing ideas and debating topics, also helps maintain cognitive function. Just like physical exercise keeps the body strong, mental exercise keeps the brain young.
9. Eating Too Fast and Overeating

Rushing through meals and frequently overeating can have serious consequences for long-term health. Studies show that eating too quickly prevents the body from recognizing fullness, leading to excessive calorie intake and weight gain. Over time, this habit increases the risk of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. Additionally, eating large portions strains the digestive system, contributing to bloating, acid reflux, and poor nutrient absorption. When the body constantly processes more food than it needs, it ages faster at a cellular level.
Practicing mindful eating can counteract these harmful effects. Eating slowly, chewing food properly, and savoring flavors help the body regulate hunger and digestion. Research suggests that people who eat mindfully consume fewer calories and maintain healthier weights. Avoiding distractions like TV or smartphones during meals can also improve digestion and prevent overeating. Making conscious choices about food intake not only promotes longevity but also enhances overall well-being.
10. Not Drinking Enough Water

Chronic dehydration is a common but overlooked factor that accelerates aging and weakens the body. Water is essential for every bodily function, from digestion to circulation and cellular repair. Studies show that dehydration contributes to fatigue, kidney problems, and reduced cognitive function. Over time, inadequate water intake can lead to chronic inflammation, increasing the risk of diseases like arthritis, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Without proper hydration, skin loses elasticity, energy levels drop, and overall health declines.
Establishing a habit of drinking enough water daily supports longevity. Experts recommend consuming at least eight glasses of water per day, though individual needs may vary based on activity levels and climate. Consuming water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables can also aid hydration. Avoiding excessive caffeine and sugary drinks helps maintain proper fluid balance. Consistently staying hydrated supports organ function, mental clarity, and overall vitality.
11. Holding onto Negativity and Resentment

Carrying emotional baggage, such as anger, grudges, or resentment, has a profound impact on physical health. Studies show that chronic negativity increases stress hormone levels, weakens the immune system, and contributes to heart disease. Negative emotions trigger inflammation in the body, leading to an increased risk of conditions like high blood pressure and depression. Over time, bitterness and unresolved emotions take a toll on mental and physical well-being, leading to faster aging.
Practicing forgiveness and letting go of resentment can significantly improve health. Research suggests that people who cultivate positive thinking and emotional resilience live longer, healthier lives. Techniques such as journaling, therapy, or meditation can help process and release negative emotions. Surrounding oneself with supportive and uplifting people also improves emotional well-being. Choosing peace over prolonged anger doesn’t just feel better—it promotes longevity and a better quality of life.
12. Ignoring Regular Health Check-Ups and Screenings
Many people avoid going to the doctor unless they feel sick, but skipping regular health check-ups can lead to undetected health issues. Studies show that early detection of conditions like cancer, high blood pressure, and diabetes dramatically improves survival rates. Many life-threatening diseases develop silently, showing no symptoms until they reach advanced stages. Without routine screenings, individuals risk allowing preventable conditions to worsen. Avoiding medical check-ups is one of the most dangerous habits for long-term health.
Scheduling annual physicals and screenings helps identify potential health problems before they become severe. Simple tests like cholesterol checks, blood pressure monitoring, and cancer screenings save lives. Preventive care, such as vaccinations and lifestyle counseling, also contributes to better long-term health. Maintaining a proactive approach to medical care increases the chances of early intervention and successful treatment. Taking health seriously today can add years to life and prevent unnecessary suffering in the future.
Many daily habits that seem harmless are slowly taking years off your life. From neglecting hydration to holding onto negativity, these behaviors silently contribute to premature aging and chronic disease. The good news is that small, consistent changes can reverse many of these effects. Prioritizing movement, mental stimulation, proper hydration, and regular check-ups can dramatically improve longevity. By becoming aware of these damaging habits and making gradual improvements, you can enhance both your lifespan and quality of life.



